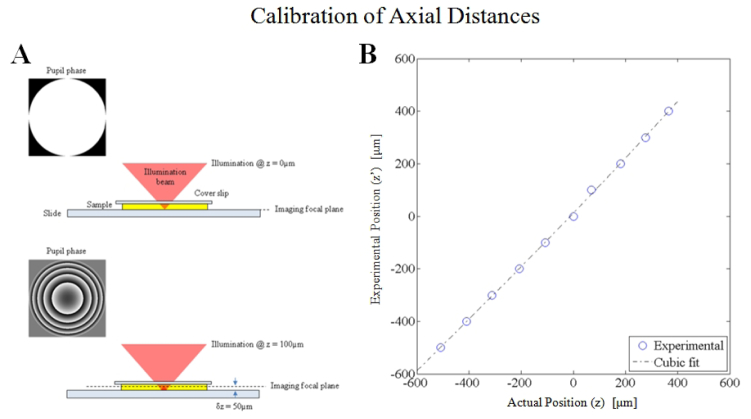
Fig. 7.
The defocus calibration method requires that the back-reflection from the sample/slide interface is in focus on the imaging path. When zero defocus phase is applied at the SLM (pupil plane), the in-focus image is at the focal plane (by definition). A defocus phase was applied at the SLM to translate the target illumination in 100µm intervals. For each defocus phase on the SLM, the sample stage is translated axially until the back-reflection is focused using the imaging path. The sample translation is recorded as the experimental z position for each expected z position. Comparison between the expected axial position versus the experimental position are shown in the plot above. The theoretical curve predicts distances which are on average 3.2% larger than the experimentally determined axial position.