Figure 3.
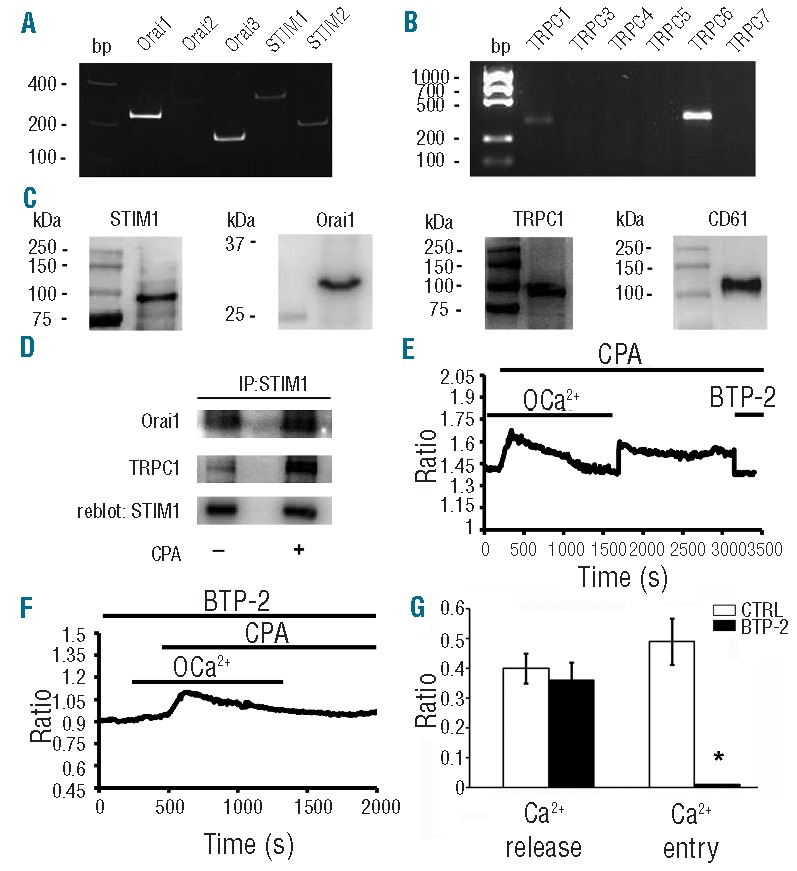
Expression and function of molecular mediators of SOCE in human Mks. (A–B) Gel electrophoresis of the PCR products for Orai, STIM and TRPC expression. PCR products were of expected size: Orai1, 257bp; Orai2, 334bp; Orai3, 159bp; Stim1, 347bp; Stim2 186bp TRPC1, 307bp, TRPC6, 341bp. No signal was observed for TRPC3/5/6/7. Representative of 3 independent experiments. (C) Protein expression of STIM1, Orai1 and TRPC1 in human CD61+ Mks at Day 13 of culture. (D) Mature Mks were treated (+) or not (−) with CPA (10 μM) and lysed. Lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-STIM1 antibody and subjected to Western blotting. Membranes were stained with antibodies against Orai1 and TRPC1 and re-blot with antibody against STIM1 to ensure equal immunoprecipitation of the protein. Representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) Intracellular Ca2+ pools were depleted by exposing the cells to CPA (10 μM) in 0Ca2+ solution. Re-addition of extracellular Ca2+ led to an increase in [Ca2+]i which was indicative of SOCE. Subsequently, acute application of BTP-2 (50 μM) inhibited CPA-elicited Ca2+ inflow, thus confirming the store-dependent nature of Ca2+ entry. (F) Pre-incubation with BTP-2 (20 μM) prevented CPA-induced Ca2+ signal on Ca2+ readdition to extracellular solution. (G) Statistical analysis of the effect exerted by BTP-2 on the peak amplitudes of both Ca2+ release and Ca2+ entry stimulated by CPA (mean±SD, n=5 independent experiments; *P<0.01).
