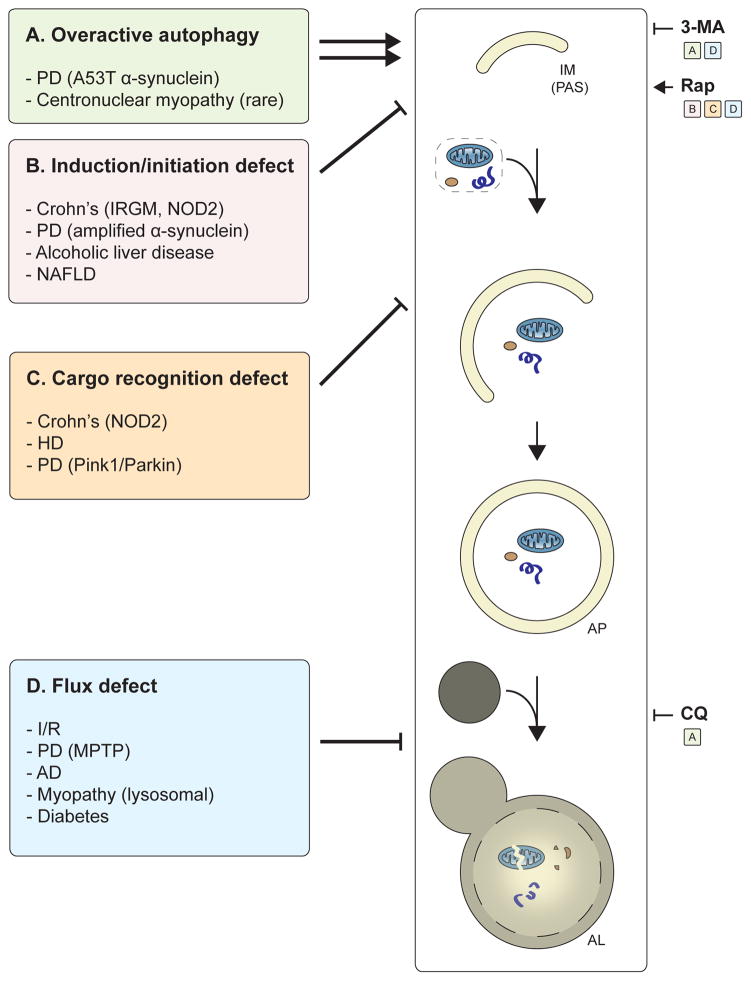
Figure 6. Summary of autophagy alterations in disease and potential treatments.
The major autophagy alterations in human disease and examples of diseases for each class are listed. (A) In diseases with “overactive” autophagy, inhibition of autophagy (via 3-MA or CQ) may provide therapeutic benefit. In diseases that lead to a defect in (B) autophagy induction/initiation or (C) cargo recognition, patients may benefit from drugs such as rapamycin (Rap) that induce autophagy. (D) In diseases that lead to a block in autophagic maturation, Rap treatment may partially restore flux and provide a cytoprotective effect. Alternatively, in diseases with a severe block in autophagic maturation, blocking autophagy at an early step (e.g., via 3-MA) may be therapeutically useful because they mitigate the cytotoxic accumulation of autophagosomes and lysosomes.