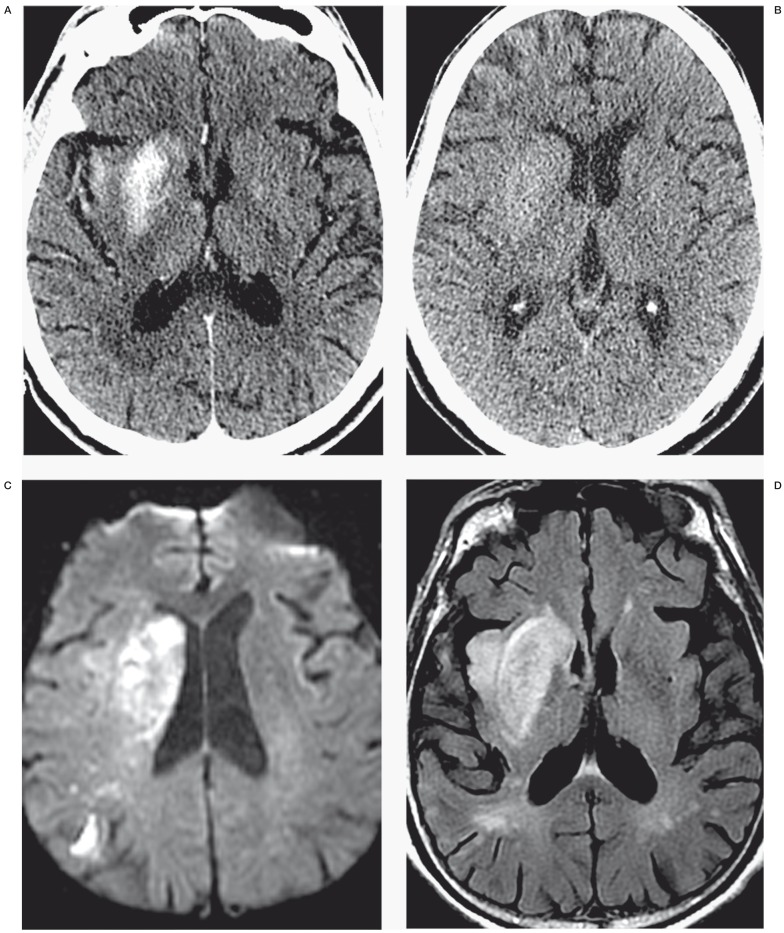
Figure 1.
Identification of contrast staining and differentiating contrast staining from hemorrhage. The first post-angiogram CT of four different AIS patients (panels A through D) demonstrates the difference between contrast staining (A,B) and parenchymal hemorrhage (C,D). Note high-density material corresponds to the right putamen and insula cortex in panel A and left lateral putamen and cortex of the left frontal and temporal lobes in panel B, without significant mass effect or surrounding edema. High density from parenchymal hemorrhage (C,D) is differentiated from contrast staining (A,B) by lack of conformation to anatomic boundaries, significant mass effect and surrounding edema. Cases presented in panels C and D also have subarachnoid hemorrhage including intraventricular hemorrhage (C), and subdural hemorrhage (D).