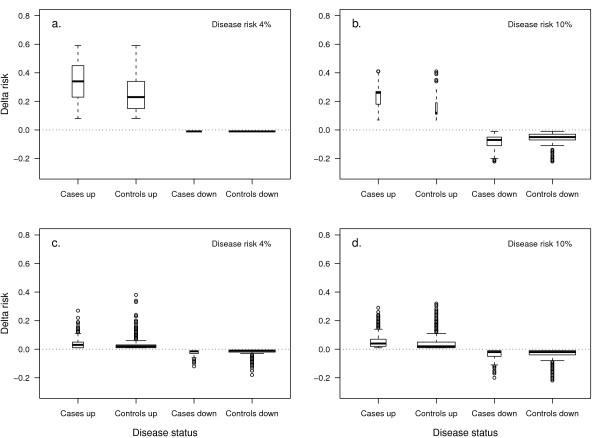
Figure 3.
Change in absolute risk at model update with rare and common genetic variants. On the × axis is shown the correct reclassification of cases and controls (that is, Cases up; Controls down) and incorrect reclassification (that is, Cases down; Controls up) when rare variants with a cumulative OR of 10 and frequency of 0.01 (Figures 3a, b) or 100 common variants each with a OR of 1.05 and a frequency of 0.30 (Figures 3c, d) are added to a baseline model with an AUC = 0.70. The bold line shows the median, the boxes indicate the interquartile ranges (range, 25-75%), and the whiskers present 1.5 times the interquartile range. Box widths are proportional to the square-root of the number of individuals in the groups. Disease risk is 4% in Figures 3a and c, and 10% in Figures 3b and d. The plot is obtained from one simulation using 200,000 individuals for Figures 3a and b, and 20,000 individuals for Figures 3c and d.