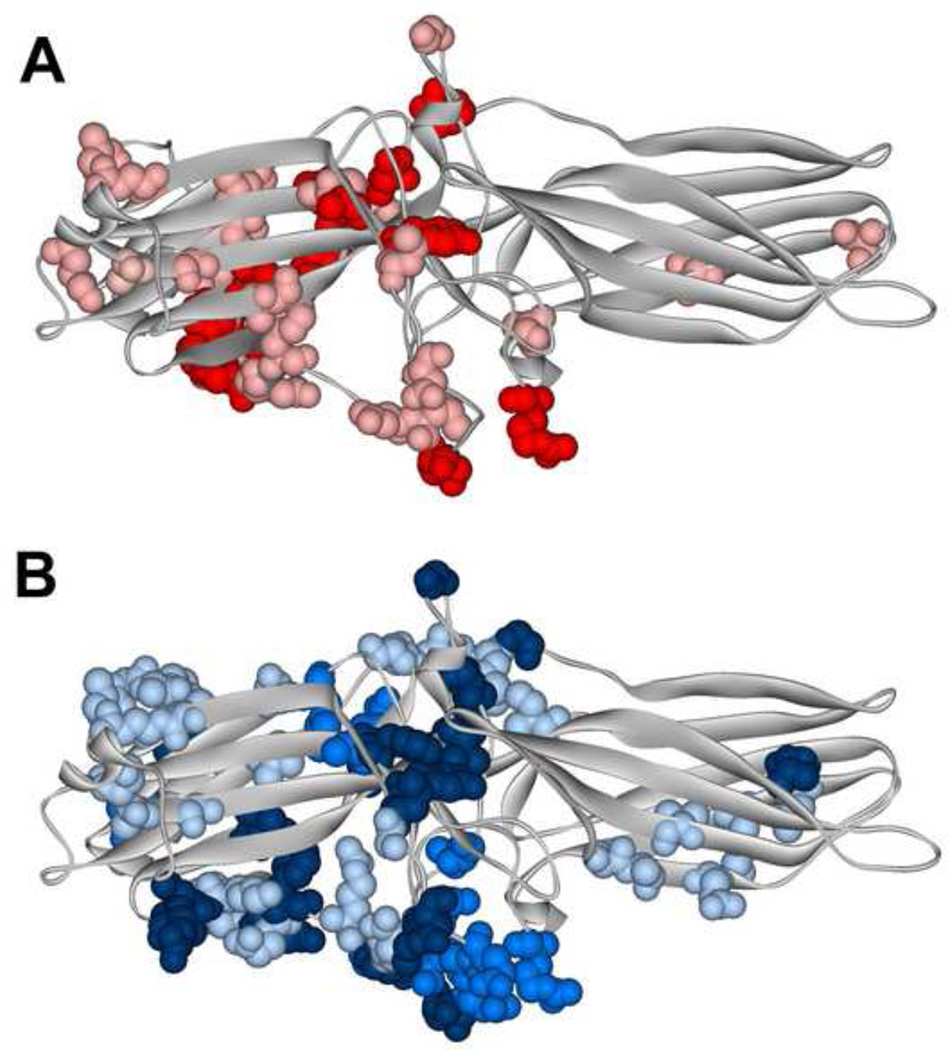
Fig. 2. Different functional forms of the same receptor engage distinct arrestin elements.
Arrestin-1 residues demonstrating significant chemical shift changes in NMR spectra upon the binding of light-activated unphosphorylated (A) or inactive phosphorylated (B). A. The magnitude of binding-induced changes is shown by color coding: bright red, shifts greater than 0.01; pink, shifts greater than 0.005, but smaller than 0.01. B. The magnitude of binding-induced changes is shown by color coding: dark blue, peaks disappeared; blue, shifts greater than 0.01; light blue, shifts greater than 0.005, but smaller than 0.01. The two forms of rhodopsin affect distinct arrestin-1 elements that only partially overlap [36].