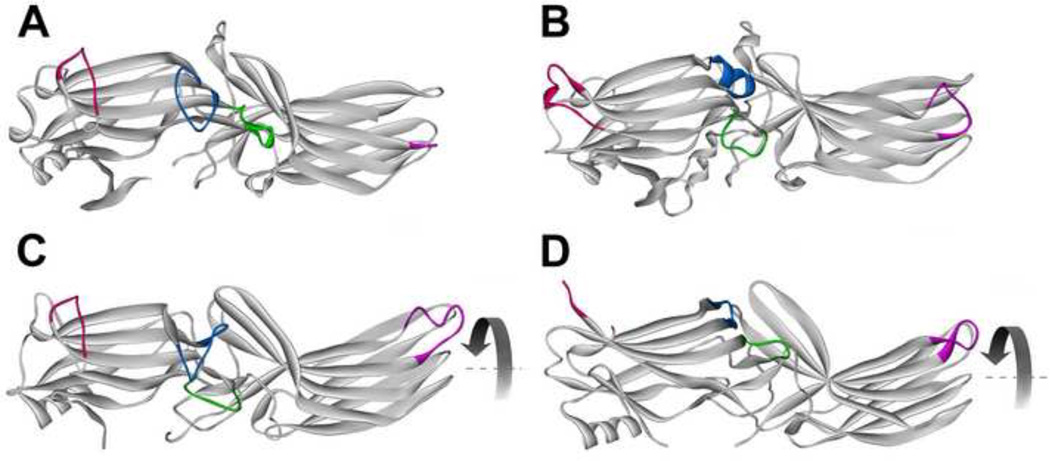
Fig. 3. Receptor binding-induced structural changes in arrestins.
A. Basal arrestin conformation (based on arrestin-2 structure 1G4M, which has the highest resolution among published arrestin structures [2]). B. A model of arrestin-1 bound to lightactivated phosphorylated rhodopsin based on intra-molecular distance measurements in free and bound arrestin-1 [38]. C. Crystal structure 4JQI of truncated arrestin-2-(1–382) in complex with multi-phosphorylated C-terminus of vasopressin V2 receptor receptor [40]. D. Crystal structure of p44, truncated splice variant of arrestin-1. Arrestin elements that change conformation upon receptor binding are color-coded, as follows: blue, the “finger loop” (G68-S78 in arrestin-1; G65-T74 in arrestin-2); green, “139 loop” (P134-S142 in arrestin-1; P131-A139 in arrestin-2); red, “157 loop” (H155-P165 in arrestin-1; E152-H159 in arrestin-2); magenta, “344 loop” (S336-S344 in arrestin-1; S330-S340 in arrestin-2). Residue numbers for corresponding bovine proteins are given. The rotation of the two domains relative to each other by 20–21° is indicated by curved arrow in C and D.