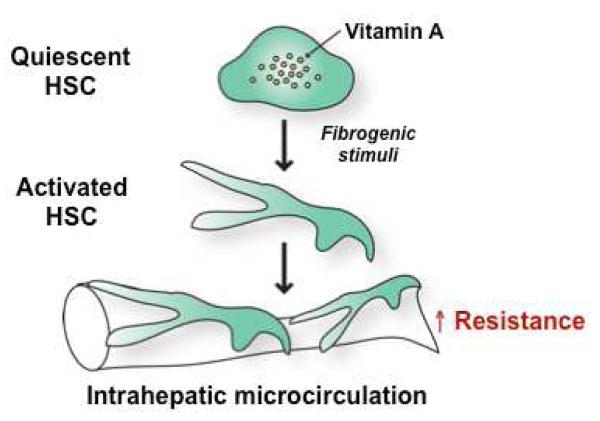
Figure 2. Activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) in liver cirrhosis increase intrahepatic vascular resistance.
Quiescent HSCs are vitamin A storage cells and found in normal livers. In response to fibrogenic stimuli, such as transforming growth factor beta, HSCs are activated to become myofibroblasts, which exhibit a contractile and fibrogenic (collagen-producing) phenotype. These activated HSCs, located underneath liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, exert a contractile effect on the hepatic microcirculation, resulting in an increase in intrahepatic resistance.