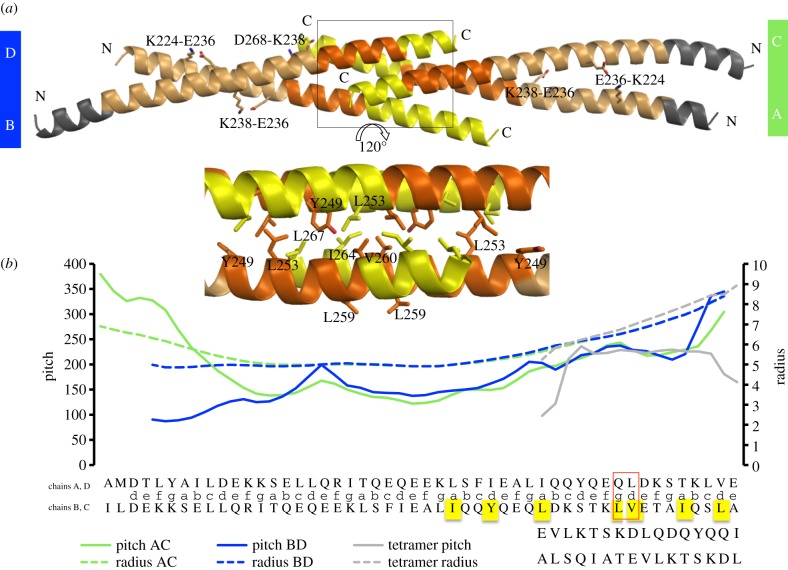
Figure 3.
(a) Crystal structure of MuRF1CC, where helices have been coloured to indicate: no interchain assembly (grey), parallel interaction (beige), antiparallel interaction (yellow), simultaneous parallel and antiparallel interaction (orange). Salt bridges are labelled. The inset (central panel) shows the hydrophobic core formation of the tetrameric region. (b) Twister analysis of each MuRF1CC half. The structural point to which the values correspond is indicated by the sequence (in dimeric or tetrameric state) displayed in the x-axis. Solid lines indicate pitch and dashed lines radius. The pitch and radius vary along the length of the molecule, but the values of the central region of each dimeric half are close to those of a canonical dimeric CC, where pitch approximates 150 Å and radius 5 Å [30]. The analysis of knobs-into-hole packing of each dimer using SOCKET [29] indicated that 18 residues in the AC dimer exhibited a conventional CC packing (7,7,4 repeat), while the BD dimer had 25 residues in CC arrangement (7,7,7,4 repeat) (electronic supplementary material, figure S1). In the sequence that follows from this, TWISTER shows the opening of the coil and a resulting helical phase transition (between residues 252-QL-253 in chains A and D, respectively, partnered to chains C and B at motif 259-LV-260; highlighted by a red box) that defines the switch from a dimeric to a tetrameric association.