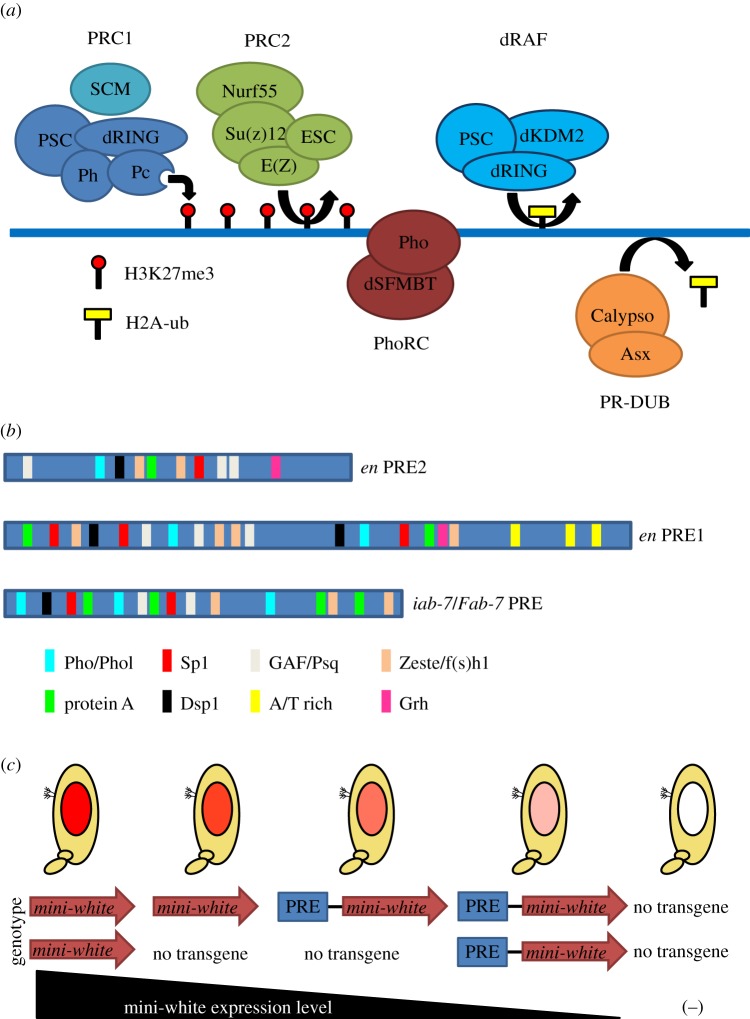
Figure 3.
PcG complexes, PRE architecture and pairing-sensitive silencing (PSS). (a) Multiple polycomb group complexes have been characterized: Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 and 2 (PRC1, PRC2), Pho-repressive complex (PhoRC), dRING-associated factors (dRAF) and Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase (PR-DUB). E(z) catalyses trimethylation of histone 3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3). The chromodomain of Pc is known to recognize this mark. Pho (and the related Phol) are the only PcG proteins to have characterized sequence-specific binding. dRING (also called Sce, Sex combs extra) catalyses H2A ubiquitination in the context of the dRAF complex, but not in the context of PRC1. The PR-DUB complex removes this H2A ubiquitination. The reason for ubiquitination cycling on H2A is not fully understood. Adapted from Schwartz & Pirrotta [53]. (b) The engrailed PREs and the iab-7/Fab-7 PRE are schematized with identified consensus sequences for various DNA-binding factors. Despite the large number of potential interactors, no single motif is sufficient to predict PREs. Adapted from Brown & Kassis [54]. (c) PSS is a phenomenon in which expression of a homozygous transgene that contains a PRE is less than in the heterozygous case, suggesting that homologue pairing enhances silencing mediated by the PRE. In comparison, homozygosity for transgenes lacking PREs generally leads to higher expression levels. The gradation of expression is schematized for a mini-white transgene in a white–/− genetic background. The white gene is responsible for red eye colour in flies.