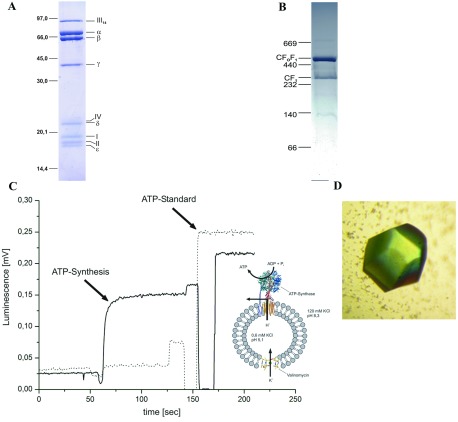
Figure 1. Biochemical and functional characterization of the purified chloroplast F-ATP synthase.
(A) SDS gel (14% total acrylamide and 4% cross-linked acrylamide) of the purified CF1FO-ATP synthase from spinach chloroplasts. The gel reveals the F1 subunits α3β3γδε and the CFO subunits b, b’, c and a, respectively, which are also called I, II, III and IV in plants. Subunit c (III) migrates as a 14-protomer entity. (B) BN gel Coomassie Brilliant Blue stained of 30 μg CF1FO-ATP synthase isolated from spinach chloroplasts. (C) ATP synthesis activity of CF1FO-ATP synthase of Spinacea oleracea. The graph demonstrates the generation of ATP, induced by an electrochemical H+/K+ gradient. To demonstrate that ATP is only produced by the ATP-synthase, the measurements were also performed with CF1FO-ATP synthase inhibited by DCCD treatment before reconstitution (dotted line). (D) Crystal of the c-ring from spinach chloroplast CF1FO-ATP synthase.