Figure 1. Potentiation of ethionamide by targeting EthR.
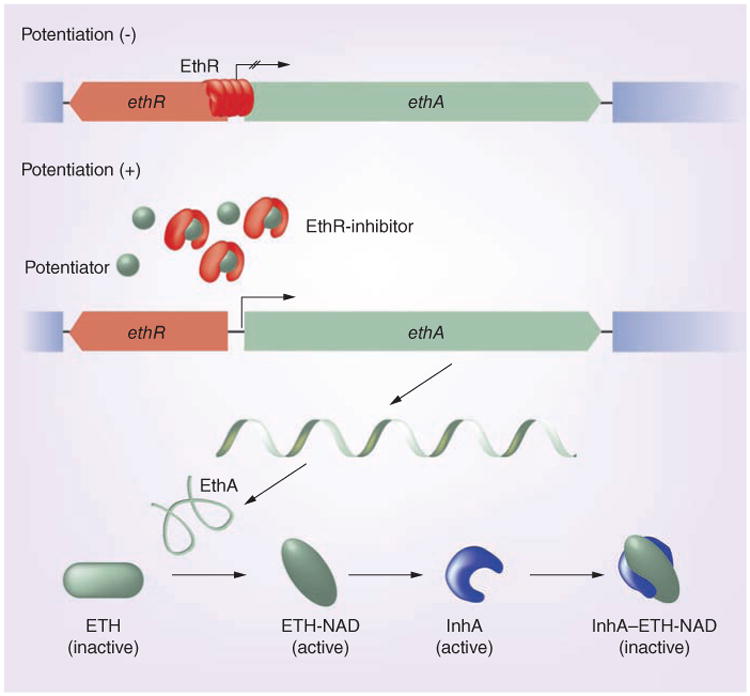
The binding of inhibitors releases EthR from its interaction with the ethA promoter. This derepresses the flavoprotein EthA, which is responsible for oxidizing and thus converting ETH to its active form, ETH-NAD. The activated drug then binds to InhA and inhibits its activity in mycolate biosynthesis. EthR inhibitors could thereby function as ETH potentiators.
ETH: Ethionamide.
Adapted with permission from [15].
