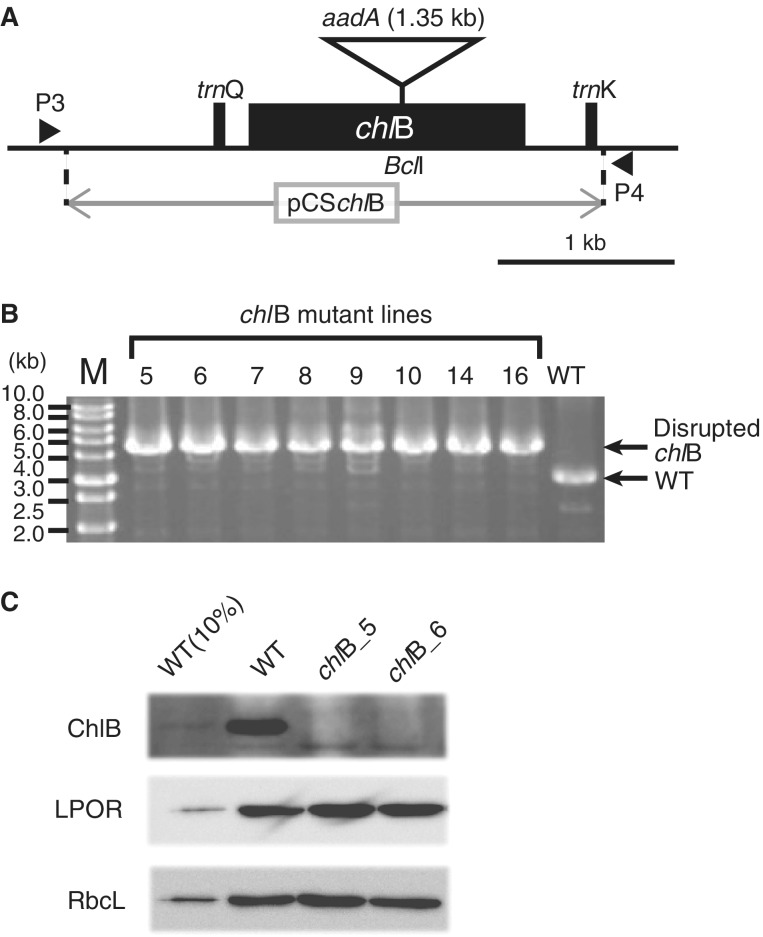
Fig. 2.—
Preparation of chlB mutant in Marchantia polymorpha. (A) Gene structure around chlB in the M. polymorpha chloroplast genome. Black boxes and horizontal line indicate exons and intergenic region, respectively. Solid triangles show primer positions designed for the confirmation of the aadA cassette insertion. A restriction enzyme (BclI) site within the chlB coding sequences shown with a triangle is the position of the aadA cassette insertion. Black angles and the triangle are not to scale. (B) Genotyping for the confirmation of homoplasmic transplastome in the chlB mutant. P3 and P4 primer pairs detected WT plastome and/or transplastome defective in the chlB (3,165 bp in WT and 4,520 bp in chlB mutant). (C) Immunoblotting analysis of ChlB protein accumulation. Samples containing 0.5 μg chlorophyll (Chl) crude chloroplast fraction proteins were loaded. In the case of WT, 0.05 μg Chl crude chloroplast fraction proteins (10% WT) were loaded to confirm the limit of detection by each antibody. The proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the blots were probed with specific antibodies against ChlB (a subunit of DPOR), LPOR, and rbcL (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit).