Fig. 2.—
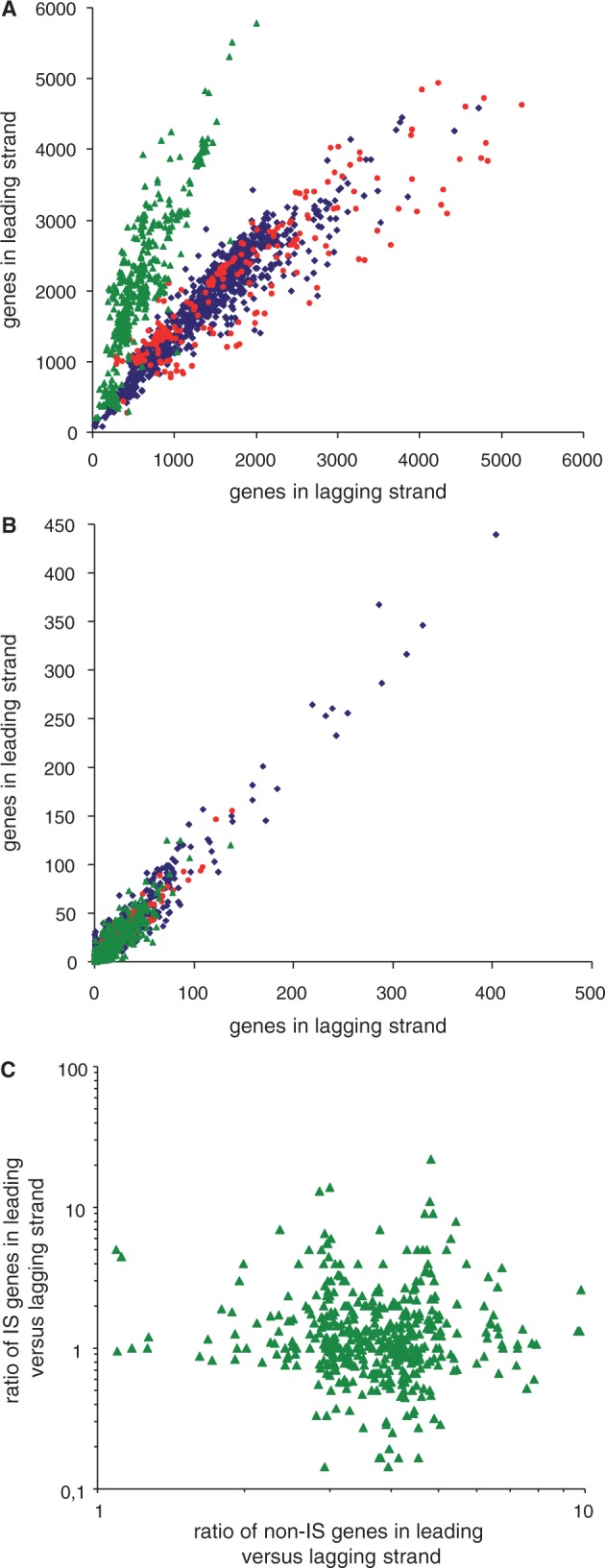
Global gene orientation for 1,727 circular bacterial chromosomes. (A) General gene orientation excluding IS-related and RNA-encoding genes. The chromosomes of four major bacterial phyla are represented: Proteobacteria (blue diamonds, 1,009 chromosomes, 3,067,992 genes, leading/lagging strand ratio = 1.07, R2 = 0.89), Actinobacteria (red circles, 224 chromosomes, 837,682 genes, ratio = 0.79, R2 = 0.82), and Firmicutes and Tenericutes (green triangles, 494 chromosomes, 1,287,236 genes, ratio = 2.58, R2 = 0.76). (B) Orientation of IS-related genes (transposases and associated factors) in genomes for the Proteobacteria (44,504 transposase genes, ratio = 1.05, R2 = 0.94), Actinobacteria (9,202 transposase genes, ratio = 1.00, R2 = 0.92), and Firmicutes and Tenericutes (17,255 transposase genes, ratio = 0.97, R2 = 0.79). (C) Correlation between the ratios of IS-gene orientation and no-IS gene orientation is inexistent in Firmicutes.
