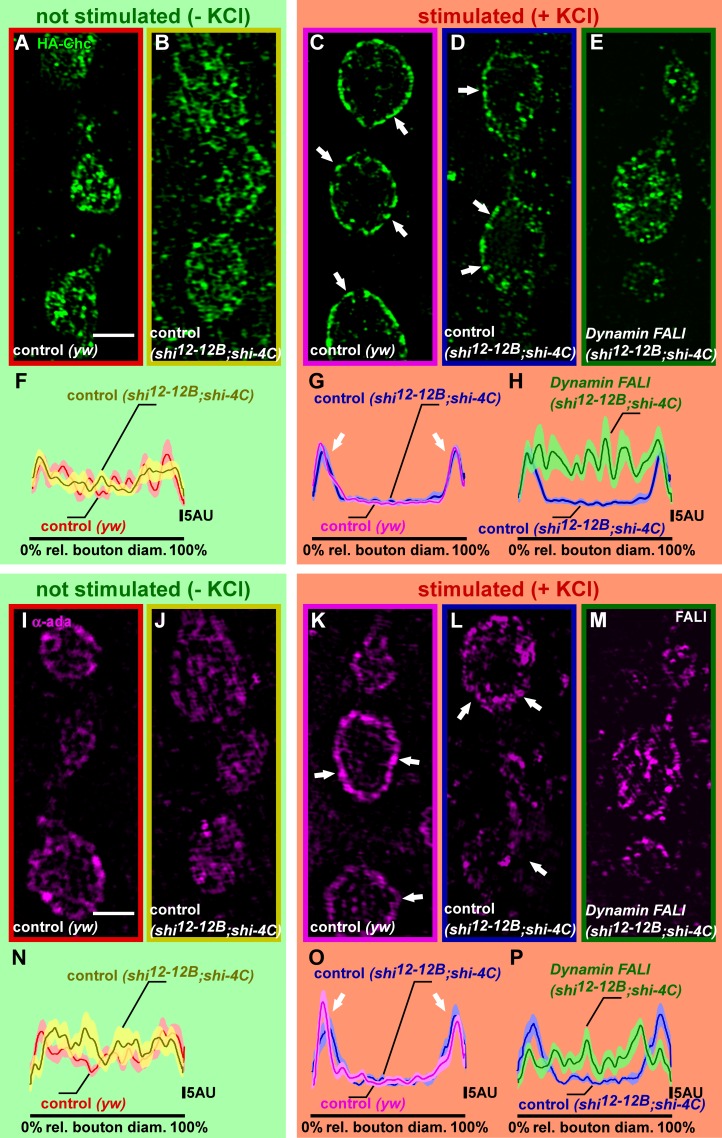
Figure 5.
Stimulus-dependent Chc and α-Ada recruitments are blocked upon Dynamin photoinactivation. (A–H) Superresolution imaging of HA-Chc fusion proteins with anti-HA antibodies, using structured illumination microscopy in not stimulated (−KCl) and stimulated (+KCl; 90 mM for 5 min) preparations. (A and B) Labeling of yw; HA-chc controls (yw) and shi12-12B/Y; HA-chc/shi-4C without FALI at rest (−KCl). Note the presence of Chc in the bouton center and at the bouton periphery as quantified in F (n = 10 boutons from three larvae); see Materials and methods and also Fig. S3. rel., relative. (C–E) Labeling of yw; HA-chc (yw) and shi12-12B/Y; HA-chc/shi-4C, stimulated with KCl without Dynamin inactivation (blue; C and D) and with Dynamin inactivation using FALI (E). Note that in the stimulated controls (C and D), Chc becomes more concentrated in the bouton periphery than in animals in which Dynamin was inactivated (E) as quantified in G and H (n = 11–12 boutons from four to five larvae); see Materials and methods and also Fig. S3. (I–P) Superresolution imaging of α-Ada using structured illumination microscopy in not stimulated (−KCl) and stimulated (+KCl; 90 mM for 5 min) preparations. (I and J) Labeling of yw controls (yw) and shi12-12B/Y; shi-4C/+ without FALI at rest (−KCl). Note the presence of α-Ada in the bouton center and at the bouton periphery as quantified in N (n = 9–10 boutons from three to four larvae); see Materials and methods and also Fig. S3. (K–M) Labeling of yw (yw) and shi12-12B/Y; shi-4C/+, stimulated with KCl without Dynamin inactivation (blue; K and L) and with Dynamin inactivation using FALI (M). Note that in the stimulated controls (K and L), α-Ada becomes more concentrated in the bouton periphery than in animals in which Dynamin was inactivated (M) as quantified in O and P (n = 9–10 boutons from four to five larvae); see Materials and methods and also Fig. S3. SEM is shown in the lighter shade. Arrows, plasma membrane. Bars, 2 µm.