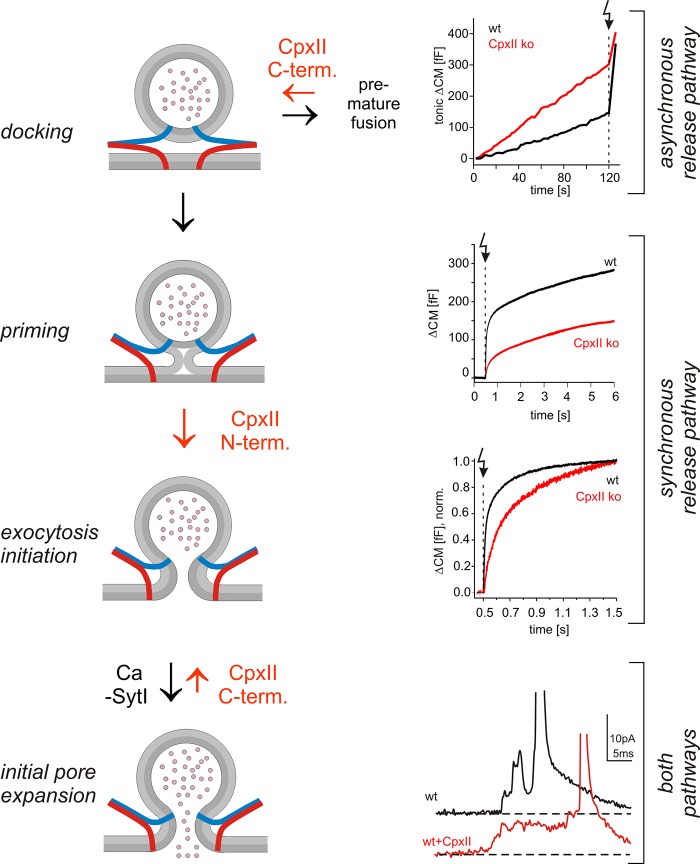
Figure 8.
Hypothetical model of Cpx action in vesicle exocytosis. The CpxII C terminus hinders premature fusion of docked vesicles through an asynchronous pathway and thereby increases the primed vesicle pool. Additionally, its N terminus speeds up fusion of primed vesicles, providing two independent, synergistic functions of CpxII to enhance synchronous release. Clamping of premature exocytosis by CpxII C terminus is continued from docking until fusion pore opening, most likely by hindering SNARE assembly (v-SNAREs, blue; t-SNAREs, red). Ca-bound SytI efficiently releases the clamp upon fusion pore opening in wt cells, as suggested by the Syt ko phenotype, CpxII overexpression, and experiments with lowered [Ca]i (Fig. 6). Arrow (dotted line) indicates flash. norm., normalized; term., terminus.