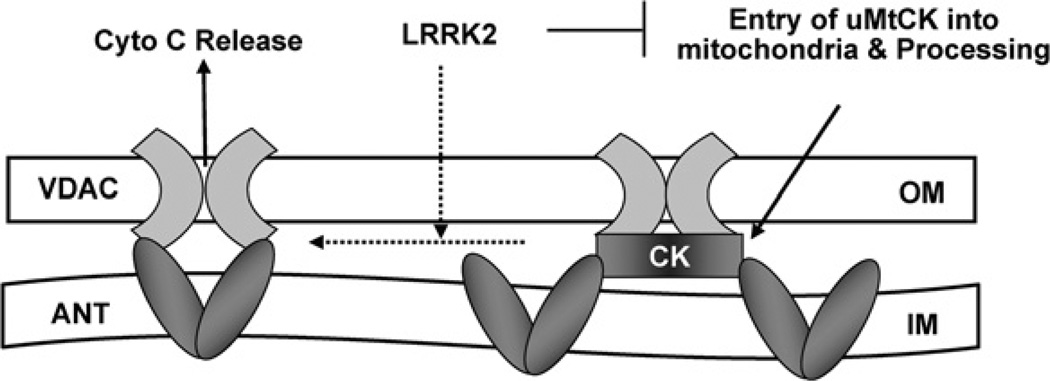
Figure 5. Schematic diagram showing the potential mechanism for LRRK2-induced cell death.
Overexpressed LRRK2 can bind to uMtCK directly and prevent it from entry into mitochondria for processing and thus inhibit mitochondrial energy channelling. Meanwhile, the lack of uMtCK in mitochondria leads to an increased interaction between ANT and VDAC, and subsequent PT pore opening, release of Cyto C and neuronal apoptosis.