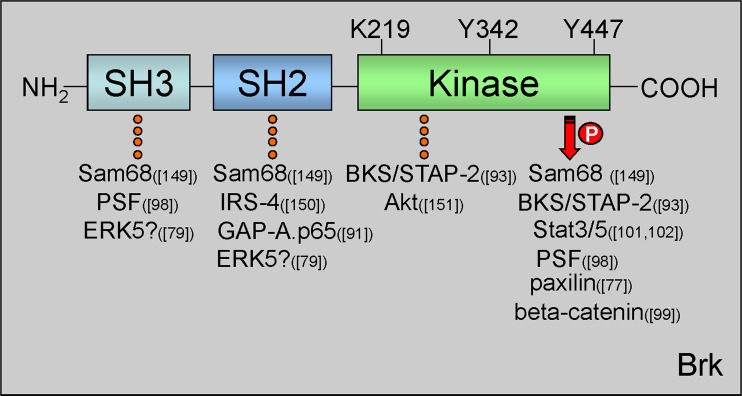
Fig. 2.
Brk protein domains and important regulatory residues. Brk protein structure consists of one N-terminal SH3 domain, one SH2 domain, and a C-terminal kinase domain. Within the kinase domain are three residues important for Brk kinase activity. Lys219 (K219) in the ATP binding pocket is required for kinase activation. Mutation of this site to Met (M) renders Brk kinase-inactive. Tyr342 (Y342) is autophosphorylated upon Brk activation. Tyr447 (Y447) is required for Brk autoinhibition. Substitution of Y to Phe (F) at this site mimics phosphorylation and results in a constitutively active Brk molecule. Brk domain-specific interacting proteins are indicated with dotted line and substrates with arrow; references to the specific proteins are reported in parenthesis [76, 78, 90, 92, 97, 98, 100, 101, 148–150]. PTB polypyrymidine tract, PSF protein-associated splicing factor, IRS-4 insulin receptor substrate 4, BKS/STAP2 breast tumor kinase substrate