Figure 2.
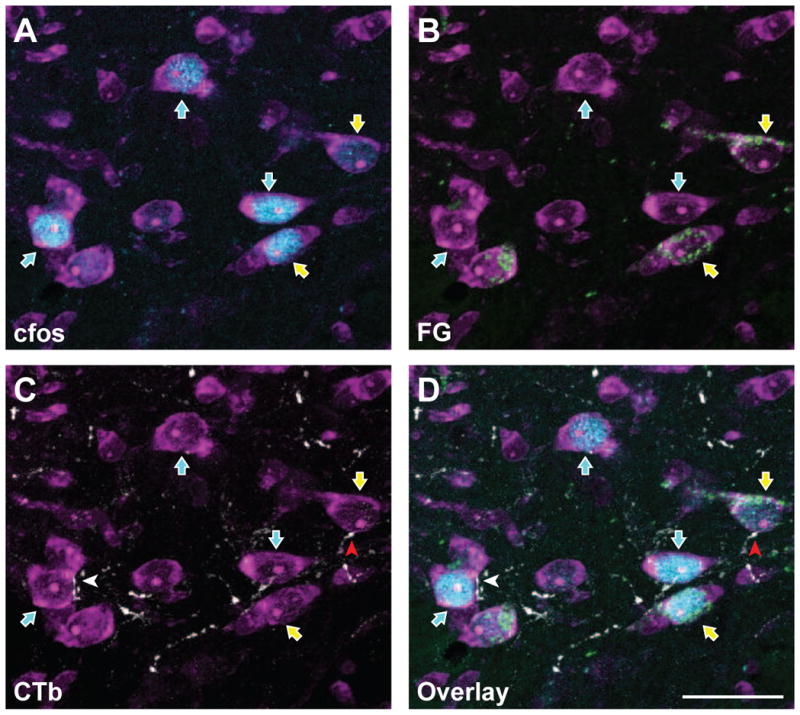
FluoroGold and c-Fos are co-localized in subsets of trigeminal dorsal horn neurons that also receive corneal afferent input. Micrographs of the same area showing the detection of individual markers are shown in panels A – C, while panel D shows all three channels in a single micrograph. A. Neurons were identified with NeuroTrace fluorescent Nissl stain (magenta). A subset of these neurons are immunoreactive for c-Fos (blue; blue arrows) following noxious stimulation of the cornea. B. Immunoreactivity for FluoroGold (green) shows a distinct subset of neurons containing both c-Fos and FluoroGold (yellow arrows). Thus, these FG-containing projection neurons are also activated by noxious corneal stimulation. C. CTb-containing corneal afferents (white) are seen in apposition to select subpopulations of trigeminal dorsal horn neurons. A neuron that receives a CTb apposition and also contains FG and c-Fos is indicated with a red arrowhead. D. Overlay of all four channels showing CTb appositions with cells containing both FG and c-Fos. Each panel is composed of a Z stack of 10 consecutive images for total depth of 3.6 μm. Scale bar = 25 μm
