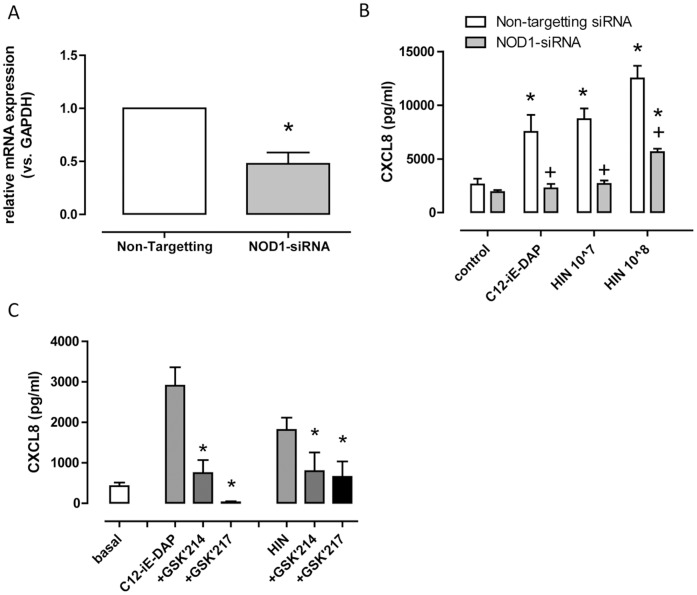
Figure 4. Effect of pharmacological inhibition of RIP2 and NOD1 siRNA mediated knockdown on responses of hESC-EC to Haemophilus influenzae (HIN) and C12-iE-DAP.
(A) Relative expression (vs. GAPDH) of NOD1 following 48 hour incubation with NOD1 siRNA normalized to non-targeting siRNA; n = 6. (B) CXCL8 release from hESC-EC following 48 hour pre-incubation with non-targeting siRNA (open bars) or NOD1-siRNA (filled bars) and 24 hour treatment +/− C12-iE-DAP (10 µg/ml) or Haemophilus influenzae (HIN) (107–108 CFU/ml); n = 7–8. (C) Effect of GSK'214 (300 nM; RIP2 inhibitor) or GSK'217 (300 nM; NOD1 inhibitor), given 30 minutes before a 24 hour treatment with HIN (107 CFU/ml) or C12-iE-DAP (10 µg/ml) on CXCL8 release; n = 4. It should be noted that GSK drugs increased CXCL8 release under basal conditions; for each experiment this was subtracted from treatment groups. For panel A, statistical significance was determined by one-sample t-test. For panel B statistical significance within siRNA groups was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test (*p<0.05), and between groups by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-test (+p<0.05). For panel C statistical significance for the effects of inhibitor of C12-iE-DAP or HIN induced CXCL8 was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test (*p<0.05).