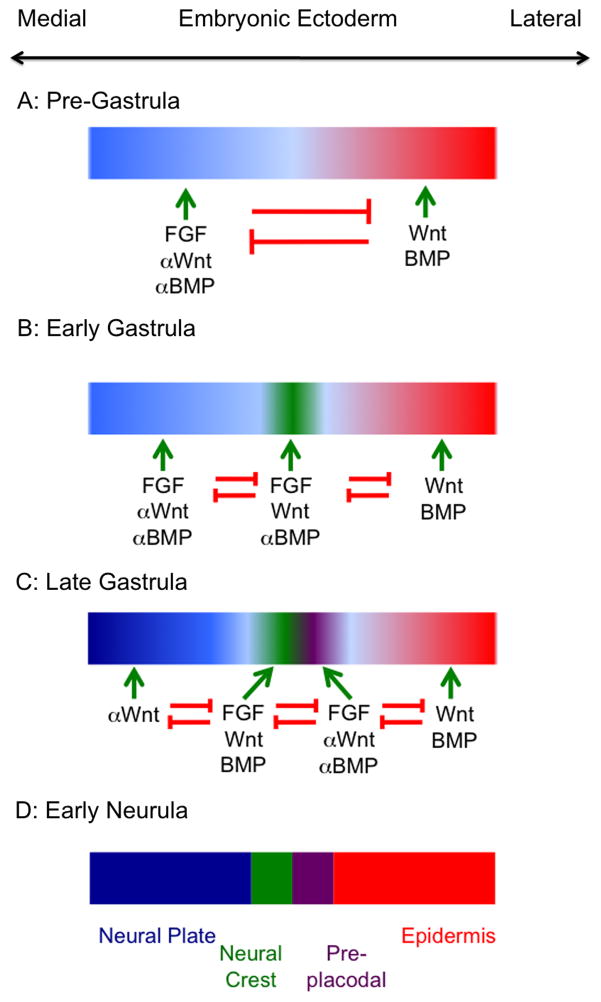
Figure 1.
A graphical summary of the signals received by embryonic ectoderm during the establishment of the neural plate, neural crest, pre-placodal region and epidermis. The diagram is a consensus of data taken from zebrafish, Xenopus, chick and mouse studies and is not intended to be an accurate representation of any one species. (A): Wnt and BMP signals in the ectoderm initiate differentiation of non-neural ectoderm, while these signals are counteracted by FGFs and BMP and Wnt inhibitors from the organizer or hypoblast. (B): Wnt and FGF signals start to induce the first neural crest genes; BMP signaling is not required for this step and may be actively inhibited. (C) Pre-placodal genes begin to be induced by FGFs and by an attenuation of Wnt and BMP signals. Wnts and BMPs begin to be expressed at the edge of the neural plate and continue to induce neural crest tissue. (D): The final resolution of the border region into four distinct regions.