Figure 2.
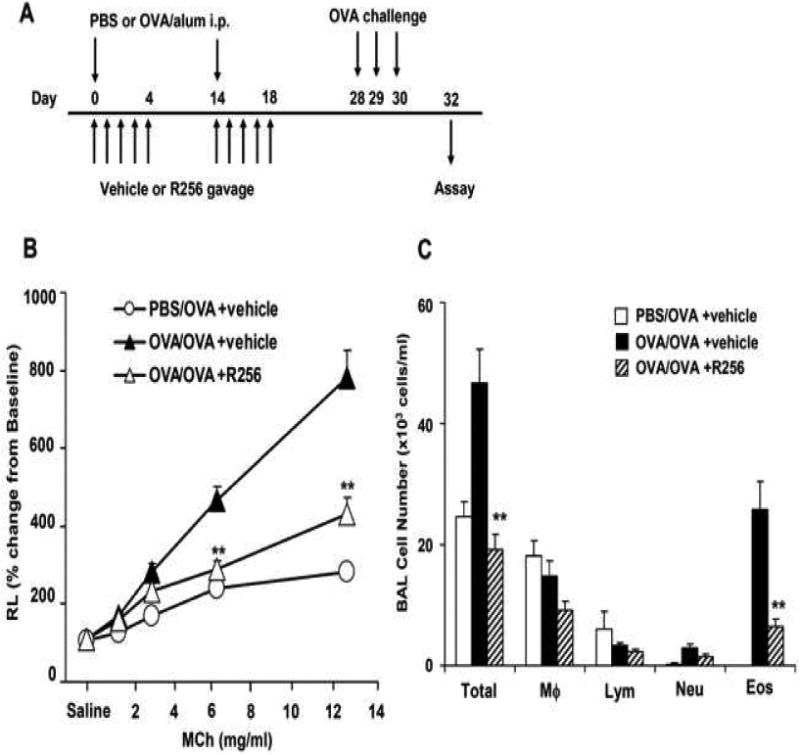
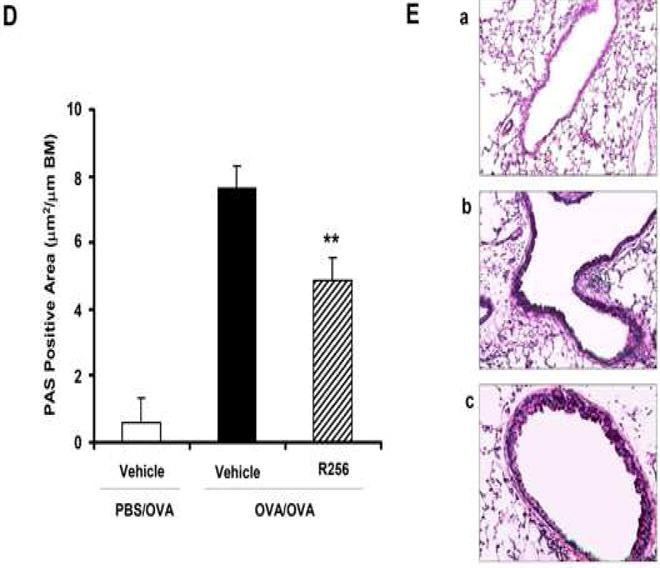
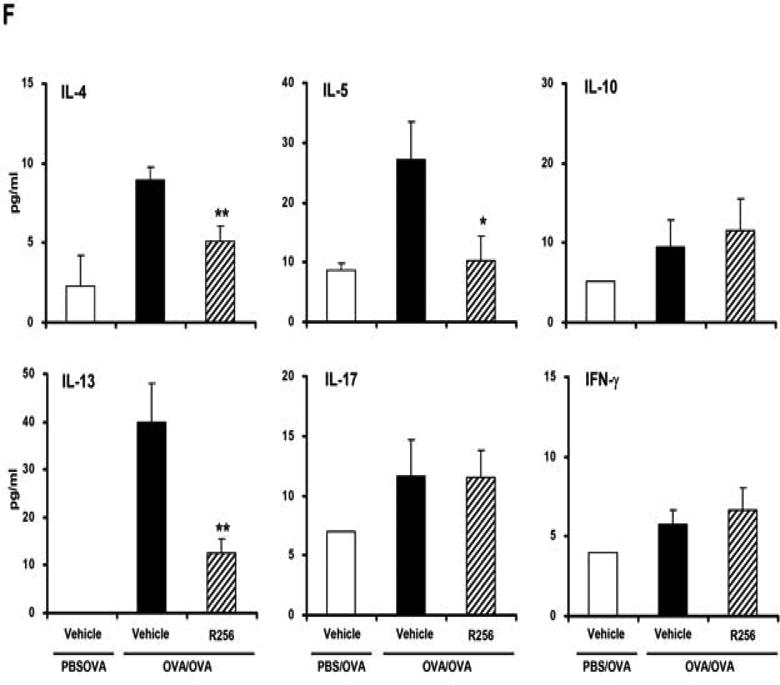
The effects of R256 treatment during allergen sensitization on the development of allergen-induced AHR and airway inflammation. (A) R256 was orally administered during the sensitization phase as described in Materials and Methods. Two weeks after the last allergen sensitization, mice were exposed to 3 consecutive days of allergen challenge followed by assessments of airway responsiveness to aerosolized MCh and BAL/lung tissue sampling 48 hrs after the last OVA challenge. (B) Lung resistance (RL). (C) BAL cell composition and (D) goblet cell metaplasia. (E) Representative pictures show (a) PBS/OVA+vehicle, (b) OVA/OVA+vehicle, and (c) OVA/OVA+R256. (F) Cytokine levels in BAL fluid. Mice were sham-sensitized and challenged to OVA (PBS/OVA) or sensitized and challenged to OVA (OVA/OVA). MCh; methacholine. Mϕ; macrophage. Lym; lymphocyte. Neu; neutrophil. Eos; eosinophil. The data for each group were expressed as means±SEM. The results are from 2 independent experiments with 4 mice per group, n=8. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 compared to OVA/OVA+vehicle-treated group.
