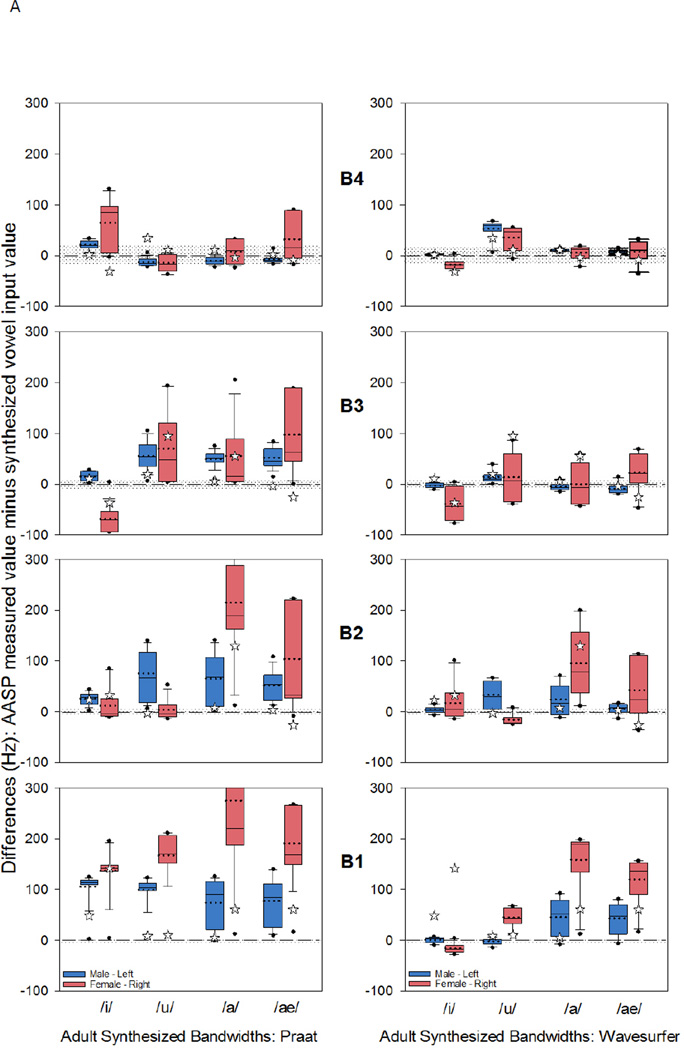
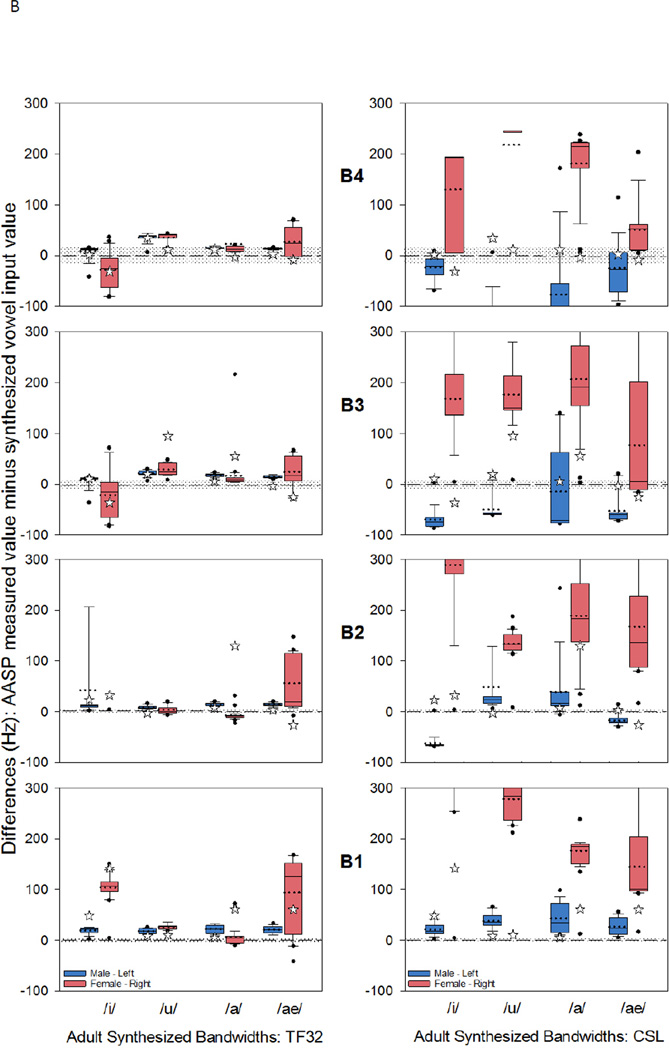
Figure 2.
A. Discrepancy scores for bandwidth (in Hz) for the four synthesized vowels. The box plots display the 25th and 75th percentile of the discrepancy scores, as well as the mode (solid line) and the median (dotted line). The whiskers display the 5th and 95th percentiles with the outlying data displayed as dots. The zero reference line is the measurement accuracy reference where zero discrepancy implies no difference between the acoustic analysis software package (AASP) measured value and the input value for the synthesized vowel. The gray region above and below the zero reference line reflects ±10% range of synthesis input value. Manually measured B1-B4 are displayed with a star symbol. Left panel displays discrepancy scores using Praat, and the right panel Wavesurfer
B. Discrepancy scores for bandwidth (in Hz) for the four synthesized vowels. The box plots display the 25th and 75th percentile of the discrepancy scores, as well as the mode (solid line) and the median (dotted line). The whiskers display the 5th and 95th percentiles with the outlying data displayed as dots. The zero reference line is the measurement accuracy reference where zero discrepancy implies no difference between the acoustic analysis software package (AASP) measured value and the input value for the synthesized vowel. The gray region above and below the zero reference line reflects ±10% range of synthesis input value. Manually measured B1-B4 are displayed with a star symbol. Left panel displays discrepancy scores using Praat, and the right panel Wavesurfer