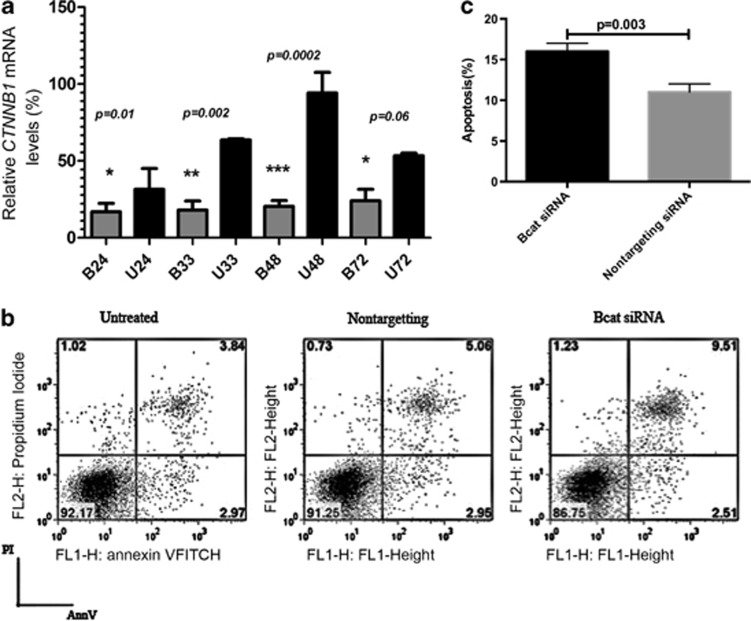
Figure 6.
β-CATENIN siRNA treatment promotes apoptosis in leukemic T cells. The cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 (Invitrogen Life Technologies) supplemented with 10% FCS, penicillin (50 U/ml) and streptomycin (50 mg/ml; both from Invitrogen Life Sciences). Molt4 cell line was transfected with 100 nM of anti-β-catenin siRNA and nontargeting control siRNA. Reduction of β-CATENIN mRNA expression was determined at 24, 33, 48 and 72 h after transfection. (a) β-CATENIN siRNA-treated samples (B24-72) compared with untreated cells (U24-72). (b) Determination of percentage of apoptotic cells by staining Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) after 48 h of treatment. Apoptotic cells defined as AnnV+ PI+ cells. Representative plots from one experiment is shown. (c) Bar plots indicate the mean value of three independent apoptosis experiments. Apoptosis rate was significantly higher (P=0.003) in β-CATENIN siRNA-treated cells as compared with controls.