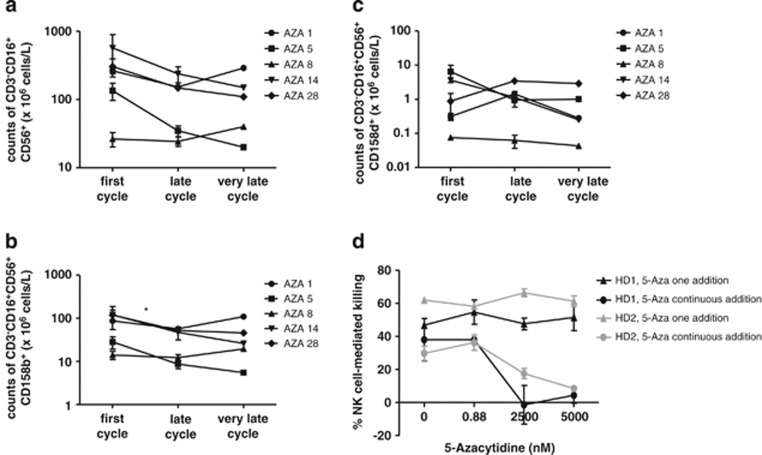
Figure 4.
Functional capabilities of NK cells affected by 5-Azacytidine in vivo and in vitro. The number and functional activity of NK cells, when further divided in subsets and measured over a longer treatment period, and the in vivo and in vitro impact of 5-Azacytidine on NK-cell functionality. (a) Absolute peripheral blood counts of CD3−CD56+CD16+ NK cells, P=0.061 for first versus late cycle. (b) Absolute peripheral blood counts of NK cells with the inhibitory phenotype CD3−CD56+CD16+CD158b+. (c) Absolute peripheral blood counts of NK cells with the activating phenotype CD3−CD56+CD16+CD158d+. (d) NK cell-mediated killing of K562 cells after 5-Azacytidine addition, either once, or every 24 h (circles, 5-Aza continuous addition) or only at the initiation of the 72 h culturing period (triangles, 5-Aza one addition). Analyses were performed on two healthy donors (black and gray symbols, respectively). K562 killing was determined by a flow cytometry-based NK cell-killing capacity assay. NK cell-mediated killing of K562 cells was compared to a negative control with no effector cells present and killing of a HLA-A3 transduced K562 line. Counts are given in 106 cells/l of blood. First cycle represents samples obtained before treatment. Significance is indicated by *P<0.05.