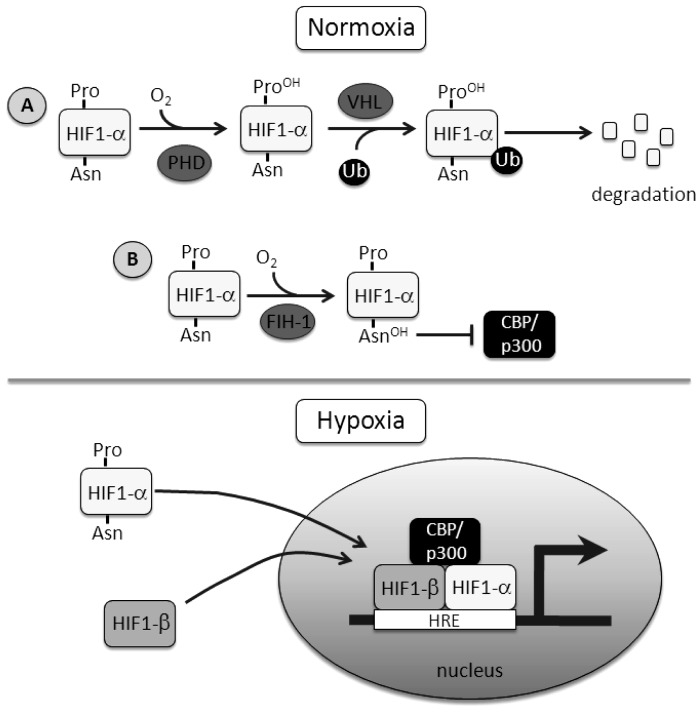
Fig. 1.
Schematic detailing the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1). A: under normoxic conditions, HIF-1α protein levels are regulated by prolyl hydroxylase domain (PHD) proteins and von Hipple-Lindau (VHL) protein, targeting the protein for degradation. B: transactivation of HIF is controlled by factor inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH-1), an asparaginyl hydroxylase. Hydroxylation of the asparagine residue prevents cofactor binding. During hypoxia, HIF-1α escapes both prolyl (Pro) and asparaginyl (Asn) hydroxylation, leading to protein accumulation, nuclear translocation, and formation and binding of the transcriptional complex to target genes. Ub, ubiquitin; CBP, CREB binding protein; HRE, hypoxia response element.