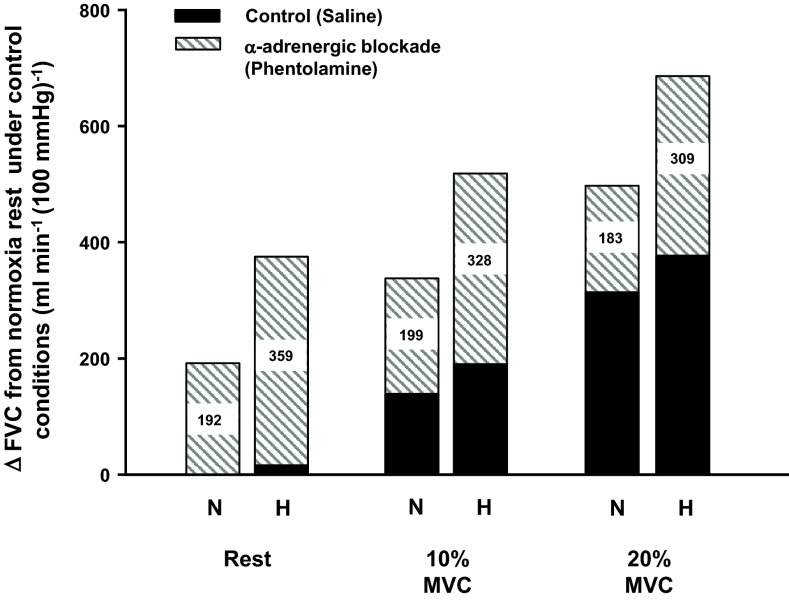
Fig. 2.
Blockade of α-adrenergic receptors via phentolamine reveals a substantial hypoxic (H) vasodilation [change (Δ) in forearm vascular conductance (FVC)] relative to respective normoxic (N) condition at rest and during rhythmic forearm contractions performed at a duty cycle of 1-s contraction and 2-s relaxation (20 contractions/min). Nos. within each bar indicate the magnitude of ΔFVC during α-adrenergic blockade compared with control (saline) conditions. MVC, maximal voluntary contraction.