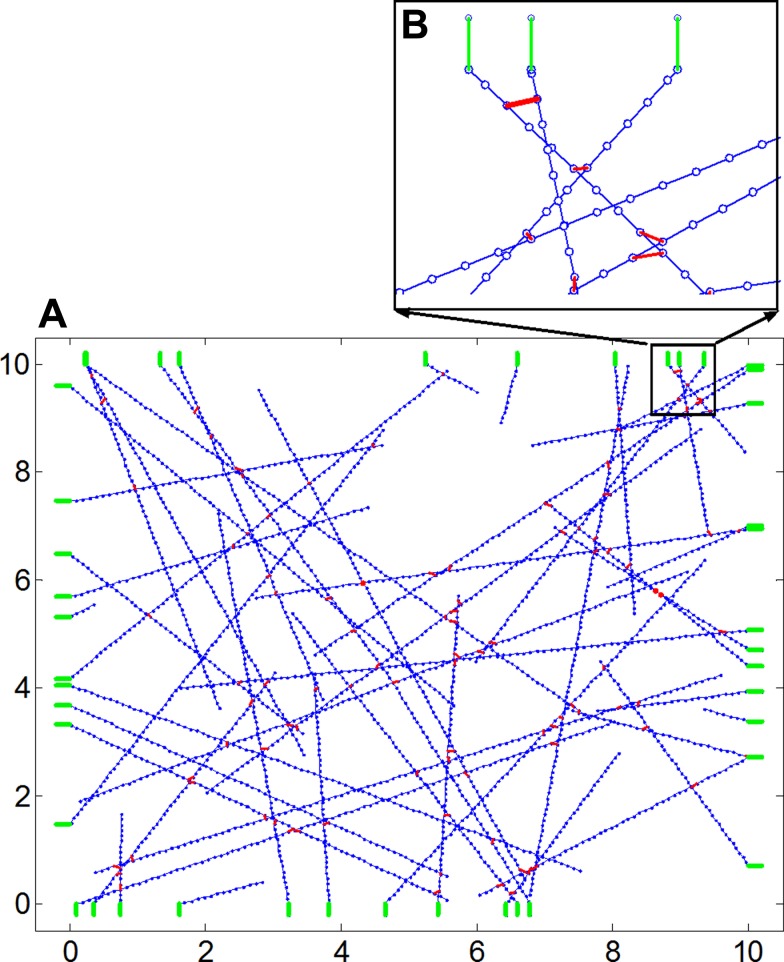
Fig. 1.
A: to create a prestressed actin network, we start with a set of actin fibers (blue) that are randomly oriented within a square space as shown. B, inset: binding sites for myosin crosslinks are added at regular intervals along each actin filament. Myosin crosslinkers can attach to binding sites on two actin filaments if the binding sites are closer than a specified distance. At points where the actin filaments intersect with the boundary, elastic elements representing the substrate material (green lines) are added to the network and represent the boundary conditions of the actin network. One end of the substrate is attached to the actin and the other end is held fixed.