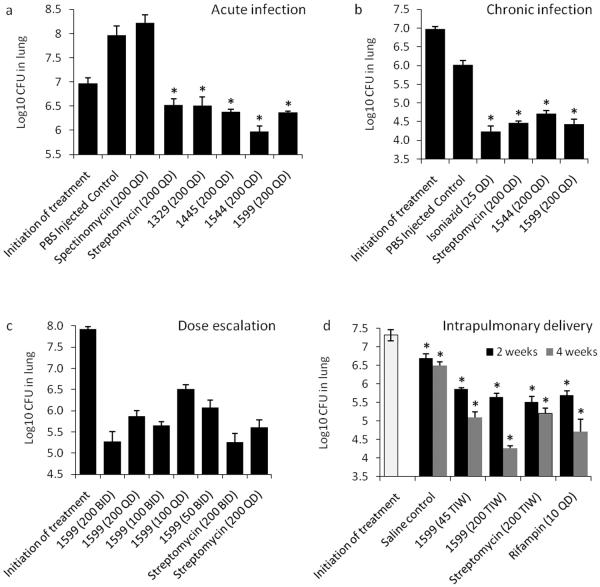
Figure 2.
In vivo efficacy trial data showing bacterial burden (log10 CFU) in the lungs of M. tuberculosis infected mice (a) M. tuberculosis–acutely infected gamma-interferon receptor knockout [IFNγ KO mice; n=5] treated with lead spectinamides and comparator drugs, all subcutaneously dosed at 200 mg/kg BID for 9 days (SEM). (b) M. tuberculosis– chronically infected immunocompetent mice (n=6) treated with lead spectinamides and streptomycin, all subcutaneously dosed at 200 mg/kg QD for 28 days (SEM). INH control was dosed at 25 mg/kg QD by oral gavage. (c) Dose ranging study on M. tuberculosis infected mice with a high bacterial load (n=6) and treated with increasing doses [mg/kg] of spectinamide 1599 or streptomycin for 28 days (SEM). (d) Intrapulmonary delivery of 1599 and streptomycin three times a week (TIW) [mg/kg] compared to rifampin dosed orally daily in M. tuberculosis– chronically infected immunocompetent mice (n=5). In panels a, b and d asterisks (*) indicate P <0.001 by pairwise multiple comparison procedures (Tukey Test).