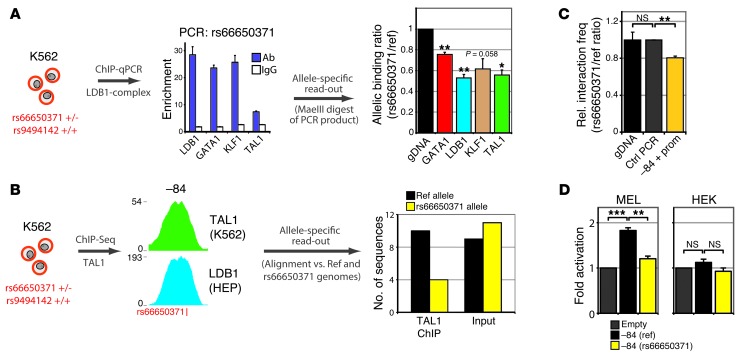
Figure 6. rs66650371 affects protein binding, chromatin looping, and enhancer activity within the erythroid HBS1L-MYB locus.
(A) Allele-specific ChIP experiments for the rs66650371 alleles in K562 cells heterozygous for this variant. Occupancy of rs66650371 (within the –84 element) by LDB1, GATA1, TAL1, and KLF1 was measured by ChIP-qPCR (n = 2, normalized against AMY2A promoter values), followed by an allele-specific read-out using MaeIII digestion (n = 2, see Methods and Supplemental Figure 4). Allelic abundance was expressed as a rs66650371 (minor)/reference (major) ratio, which was set to 1 for genomic DNA (gDNA). A ratio of less than 1 is the result of a relative lower abundance of the rs66650371 minor allele in the ChIP samples. (B) TAL1 ChIP-Seq was performed in K562 cells, and sequence reads were mapped against the reference and rs66650371 (containing the minor 3-bp deletion allele) genomes. K562 input genomic DNA was PCR amplified (amplicon spanning rs66650371) and cloned into a plasmid; colonies were sequenced (n = 20). (C) Allele-specific quantification (n = 3) of chromatin looping between the –84 element and the MYB promoter in K562 cells. A long-range PCR approach was combined with an MaeIII digestion-based read-out for quantification (see Methods). (D) Luciferase reporter assays measuring enhancer activity of the reference (ref.) and rs66650371 minor –84 enhancer alleles in erythroid (MEL) and nonerythroid (HEK) cells. Error bars display SEM. Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.