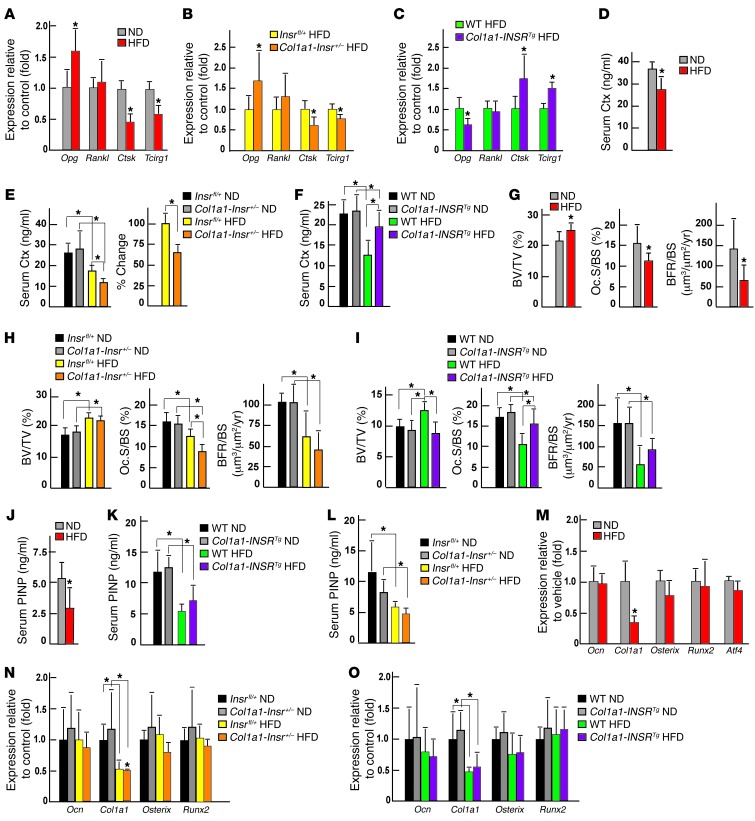
Figure 4. HFD decreases bone resorption in an insulin-dependent manner.
(A) qPCR analysis of the expression of Opg, Rankl, Ctsk, and Tcirg1 in bones of WT mice fed a normal diet or a HFD (n = 4); (B) Insrfl/+ and Col1a1-Insr+/– mice fed a HFD (n = 7); and (C) WT and Col1a1-INSRTg mice fed a HFD (n = 6). (D) Serum Ctx levels in WT mice fed a normal diet or a HFD (n = 8). (E) Serum Ctx levels in Insrfl/+ and Col1a1-Insr+/– mice fed a normal diet or a HFD (n = 8). (F) Serum Ctx levels in WT and Col1a1-INSRTg mice fed a normal diet or a HFD (n = 8). (G) Histomorphometric analysis of vertebrae of WT mice fed a normal diet or HFD (n = 8), (H) Col1a1-Insr+/– mice fed a normal diet or HFD (n = 8), and (I) Col1a1-INSRTg mice fed a normal diet or HFD (n = 8). Mineralized bone volume over the total tissue volume (BV/TV), osteoclast surface per bone surface (Oc.S./BS), and bone formation rate per bone surface (BFR/BS) were measured. (J) Serum PINP levels in WT (n = 6), (K) Col1a1-INSRTg (n = 6), and (L) Col1a1-Insr+/– (n = 6) mice fed a normal diet or a HFD. qPCR analysis of the expression of Ocn, Col1a1, Osterix, and Runx2 in bones of (M) WT (n = 4), (N) Col1a1-Insr+/– (n = 5), and (O) Col1a1-INSRTg (n = 5) mice fed a normal diet or a HFD. *P < 0.05.