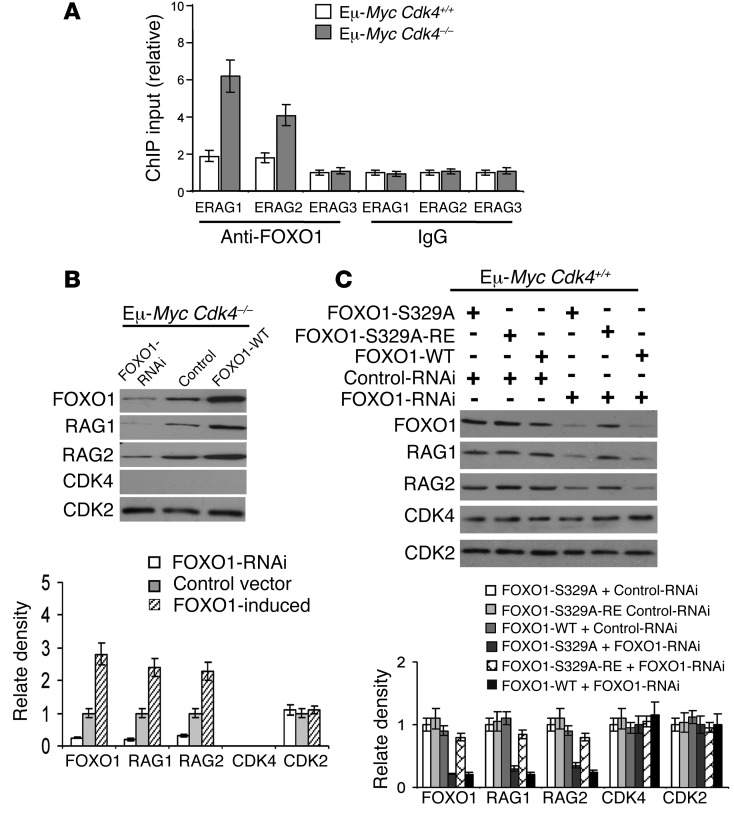
Figure 6. CDK4 deficiency induces Rag1 and Rag2 transcription via FOXO1 in Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells.
(A) ChIP analyses of FOXO1 binding to enhancers in the Rag1/Rag2 locus. ChIP was performed with anti-FOXO1 antibody or an isotype IgG control antibody, followed by qPCR analysis of FOXO1 binding to regulatory elements (ERAG1-ERAG3) in the Rag1/Rag2 locus (39, 43, 48, 65) in Eμ-Myc Cdk4–/– versus Eμ-Myc Cdk4+/+ lymphoma. Results are the fold enrichment in immunoprecipitates of FOXO1 antibody relative to control antibody (mean and SD of triplicate ChIP; P < 0.01). (B) Control of RAG1 and RAG2 expression by CDK4 is FOXO1 dependent. Eμ-Myc Cdk4–/– lymphoma cells were transfected with siRNA targeting FOXO1 (FOXO1-RNAi), a control siRNA (Ctrl RNAi), or a vector driving FOXO1 expression. Levels of FOXO1, RAG1, RAG2, CDK4, and CDK2 proteins were determined by immunoblotting. Note that FOXO1 knockdown reduced RAG1 and RAG2 levels, whereas FOXO1 overexpression increased their levels. Results shown are representative of three separate analyses. (C) FOXO1-mediated induction of RAG1 and RAG2 in Eμ-Myc B cells requires phosphorylation of S329 in FOXO1. Eμ-Myc Cdk4+/+ lymphoma cells were cotransfected with siRNA targeting FOXO1 and vectors expressing FOXO1-S329A or a wobble mutant of FOXO1-329A (FOXO1-S329A-RE) resistant to the FOXO1 siRNA. Note that FOXO1 knockdown decreased RAG1 and RAG2 levels and that this was reversed by expression of FOXO1-S329-RE. Immunoblotting with CDK4 and CDK2 showed equal loading. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Graphs display the median ± SD (n = 3; mean ± SD, with error bar).