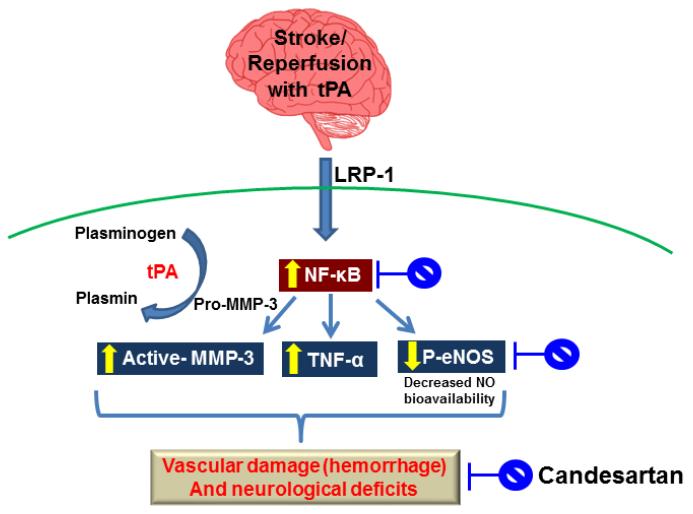
Fig. 6.
Schematic of experimental hypothesis for the possible mechanisms of candesartan-induced vascular protection. t-PA treatment induces matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) through the binding to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) and the activation of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF- κB) in endothelial cells (ECs) at the ischemic site, and t-PA activates plasmin, which in turn activates MMP-3, thereby contributing to greater vascular injury (i.e., hemorrhage) and neurological deficit. Abbreviations: tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor- α p-eNOS, phospho- endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide.