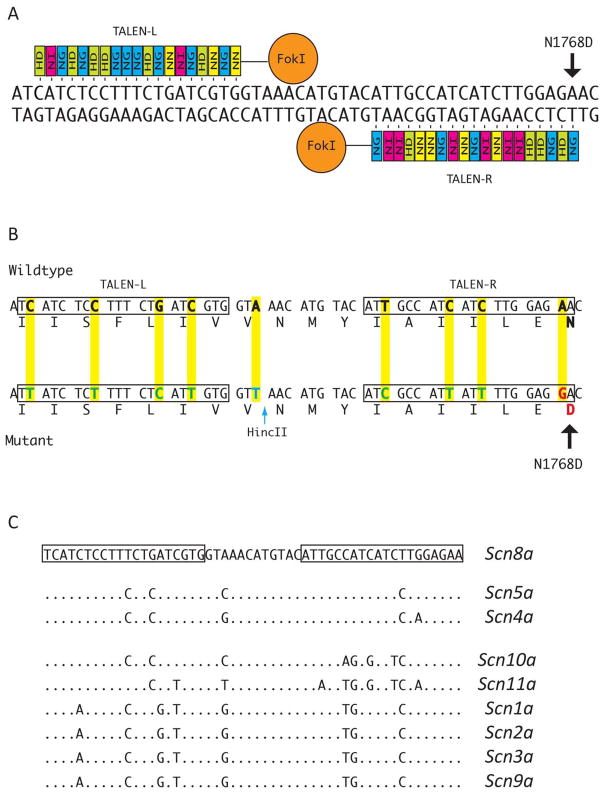
Figure 1. TALEN binding sites in Scn8a and paralogous sodium channel genes.
A. Repeat variable di-residue (RVD) sequence for left and right TALENs directing the FokI endonuclease to a site within exon 26 of mouse Scn8a. The HD residue (green) binds the C nucleotide; NI (pink) binds A; NG (blue) binds T; NN (yellow) binds G. The targeted nucleotide for introduction of the epilepsy mutation p.Asn1768Asp is marked with an arrow. B. Nine nucleotide substitutions (yellow) were incorporated into the targeting construct to prevent re-digestion after homologous recombination with the targeting construct. One substitution introduced the HincII site used for genotyping (blue arrow). C. Sequences of the TALEN targeted site in paralogs from the sodium channel multigene family. Dots represent sequence identity. The most closely related paralogous sites are in Scn4a and Scn5a, with 1 or 2 bp mismatches per TALEN binding site. The third closest site in the mouse genome is in Scn10a, with 5 mismatches in one binding site.