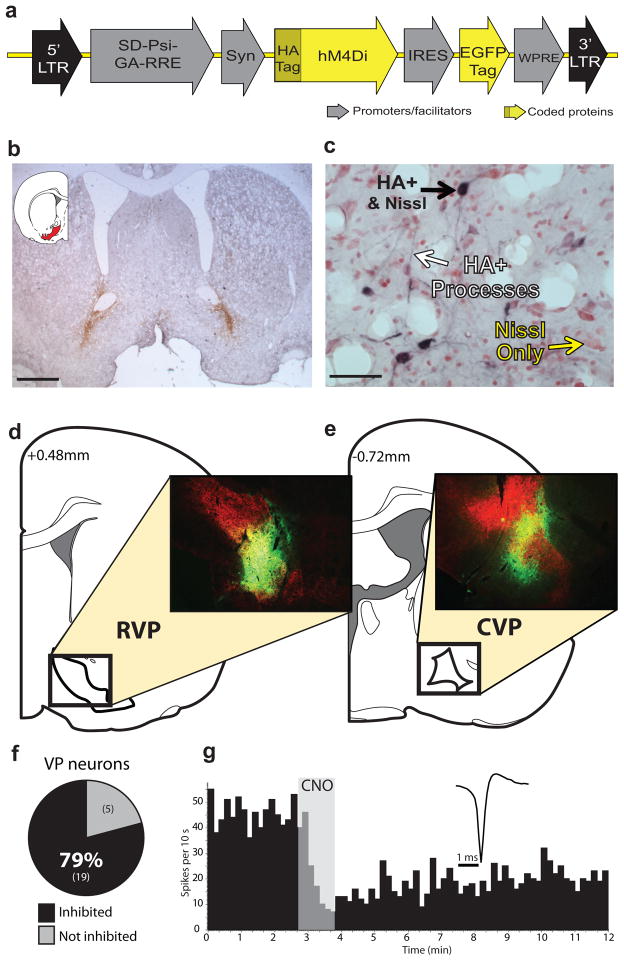
Figure 1. hM4Di inhibitory DREADD expression and function.
a) Syn-hM4Di-HA-GFP lentivirus used to express hM4Di DREADDs under a neuronal-specific human synapsin promoter (Syn) in RVP or CVP. b) Typical staining for HA-tagged hM4Di after bilateral injections into RVP. Scale bar=1 mm. c) HA-tagged hM4Di receptors are expressed on cell bodies and processes (black staining) in VP (neutral red counterstain). Scale bar=50 μm. d) Typical HA expression (green) in RVP, largely contained within VP borders (defined with SP counterstain in red). e) Typical HA expression in CVP, largely contained within VP borders (as defined in d). Images in b–e are representative of DREADD expression seen in experimental groups, ns listed in Results. f) In animals with Syn-hM4Di-HA-GFP in RVP or CVP, local application of 100 μM CNO onto extracellularly recorded VP neurons in vivo (via double barrel glass pipette) inhibited firing rates in the vast majority of neurons tested (19/24). g) Typical change in discharge rate of a VP neuron (waveform inset) after local CNO application (shaded region).