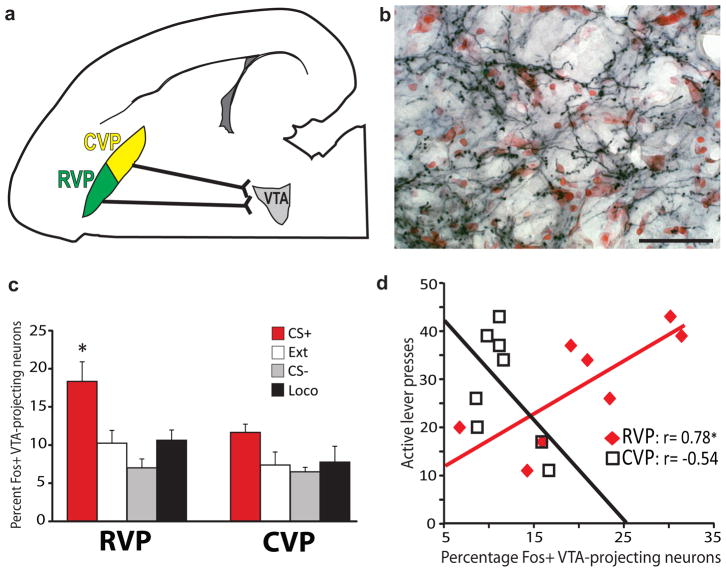
Figure 3. Rostral VP projections to VTA are Fos-activated during cued reinstatement.
a) Predominantly ipsilateral projections from RVP and CVP to VTA are diagrammed in the horizontal plane. b) Axon terminals in VTA express the anterogradely-transported, HA-tagged hM4Di receptor (black axonal processes) after Syn-hM4Di-HA-GFP injection in ipsilateral RVP (red Nissl counterstain in VTA). Coronal view, scale bar=50 μm. Image is representative of VP axonal DREADD expression in VTA of experimental animals, group ns listed in Results. c) Mean±SEM percentages of VTA-projecting (CTb+) RVP or CVP cells that express Fos after cue-induced reinstatement (CS+), or control behavioral conditions, where animals were exposed to: the extinguished self-administration environment without cues or cocaine (Ext), a tone/light stimulus not associated with cocaine (CS−), or a locomotion- enhancing novel environment (Loco). A greater proportion of VTA-projecting neurons in RVP were Fos-activated in CS+ than in control animals [*CS+ different from: Ext (p=0.01), CS− (p=0.005), and Loco (p=0.025)]. No significant behavior-specific activation of VTA-projecting neurons was detected in CVP. Bars=m±SEM. d) Cue-induced reinstatement behavior was positively correlated with Fos activation of VTA-projecting neurons in RVP (*Pearson correlation: p=0.02), but not CVP (not significant).