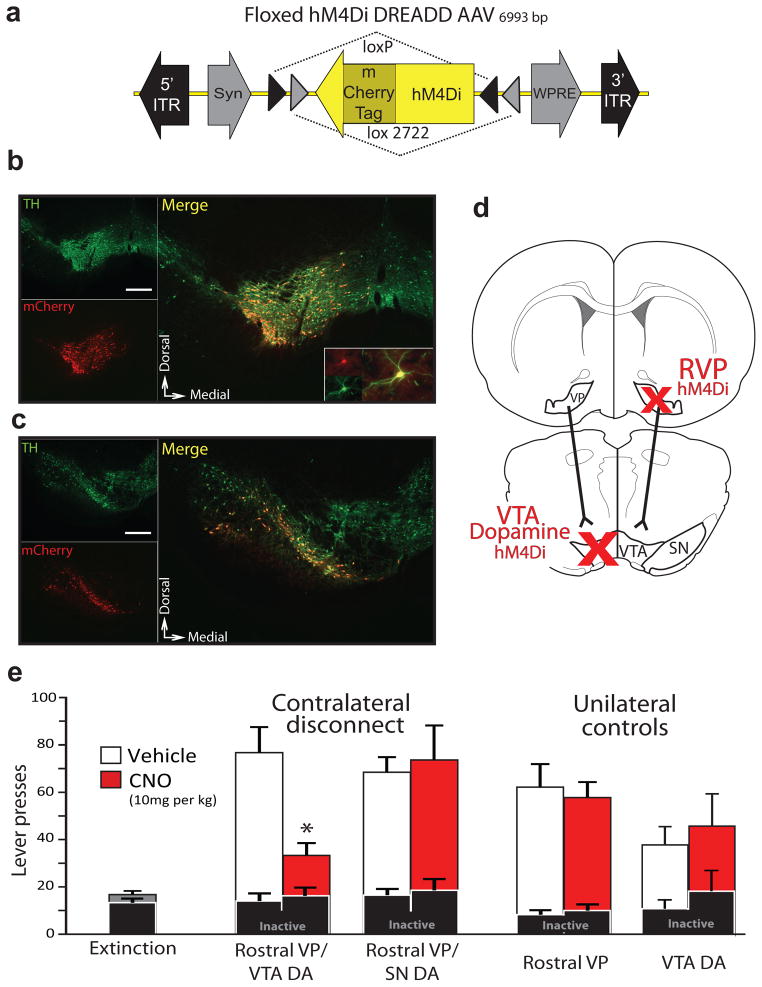
Figure 6. Functional disconnection of rostral VP projection to VTA dopamine neurons blocks cue-induced reinstatement.
a) A DIO-Syn-hM4Di-mCherry AAV construct was used to selectively express mCherry-tagged hM4Di receptors in dopamine cells in TH::Cre+ transgenic rats. b) hM4Di expression is shown in a representative animal with DIO-Syn-hM4Di-mCherry injection in VTA. Immunolabeling for TH identifies dopamine neurons (green), and mCherry (red) identifies hM4Di-expressing neurons in VTA. Nearly all hM4Di-expressing neurons were dopaminergic. VTA-injected animals did not show substantial hM4Di expression laterally in SN, or in the contralateral VTA. Scale bar=500 μm. Inset shows hM4Di+TH+ cell at high magnification. c) hM4Di expression is shown in a representative animal with DIO-Syn-hM4Di-mCherry injections in SN. Minimal expression in VTA was observed. Scale bar=500 μm. Equivalent expression observed in behaviorally tested rats; VTA n=9, SN n=8. d) Unilateral Syn-hM4Di-HA-GFP injections were made in RVP, and DIO-Syn-hM4Di-mCherry injections were made in the contralateral VTA or SN of TH::Cre+ rats, or VTA of Cre- littermates. When systemic CNO is administered, serial connectivity between VP and midbrain dopamine populations is compromised bilaterally via unilateral hM4Di inhibition of RVP, and contralateral hM4Di inhibition of dopamine neurons. e) Active and inactive lever pressing during cue-induced reinstatement in RVP/VTA dopamine contralateral disconnect animals. Pressing during late extinction (Ext., grey bar at left), and cued reinstatement after vehicle (white bars) or CNO (10 mg/kg; red bars) are shown. All contralateral disconnect animals received unilateral RVP Syn-hM4Di-HA-GFP injections, and contralateral DIO-Syn-hM4Di-mCherry injections into VTA or SN of TH::Cre+ rats. Unilateral RVP inactivation rats (RVP hM4Di) were Cre negative, and received unilateral RVP hM4Di virus, plus contralateral VTA dopamine hM4Di virus (though the latter did not cause hM4Di expression in these Cre- rats). Unilateral VTA dopamine inactivation rats (VTA dopamine hM4Di) were Cre+, and received only unilateral VTA dopamine hM4Di virus. Only contralateral disconnection of RVP from VTA dopamine neurons reduced cued reinstatement below control levels. *p<0.001. Bars=m±SEM.