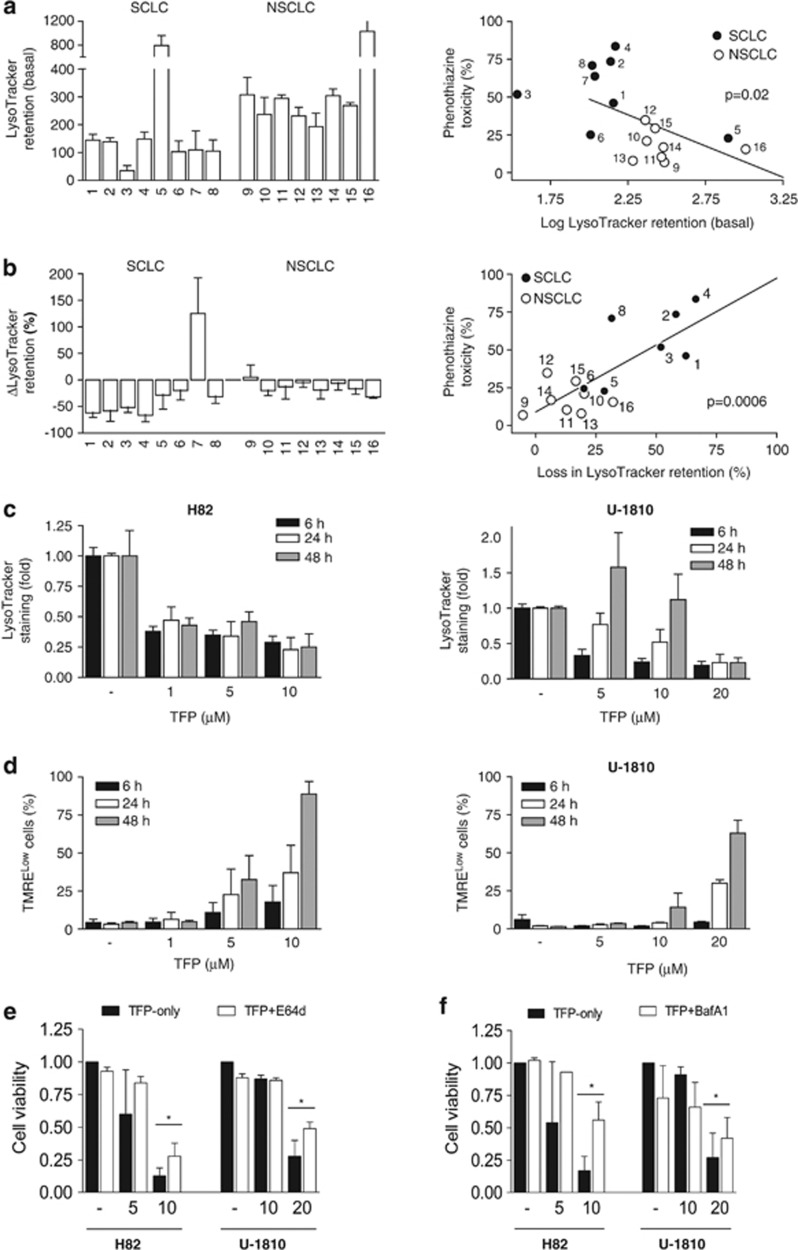
Figure 5.
Baseline and TFP-induced loss of LysoTracker retention correlate with phenothiazine sensitivity. (a) Eight SCLC (1: H69, 2: H82, 3: H592, 4: U-1285, 5: U-1568, 6: U-1690, 7: U-1906, 8: U-2020) and eight NSCLC (9: A549, 10: H125, 11: H1299, 12: H157, 13: H23, 14: H661, 15: U-1752, 16: U-1810) cell lines were collected without treatment and analyzed for baseline LysoTracker retention; correlation between baseline LysoTracker retention (log) and phenothiazine toxicity (see Figure 1) is shown on the right. (b) Cells were treated with 10 μM TFP for 24 h and thereafter analyzed for TFP-induced changes in LysoTracker retention (ΔLysoTracker); correlation between ΔLysoTracker and phenothiazine toxicity is shown on the right. (c) H82 and U-1810 cells were treated with TFP at the indicated concentrations for 6, 24 or 48 h; lysosomal pH was estimated by LysoTracker retention. (d) H82 and U-1810 cells were treated with TFP at the indicated concentrations for 6, 24 or 48 h; mitochondrial membrane potential was estimated by TMRE retention. (e) H82 and U-1810 cells were pre-treated (1 h) with E-64d (30 μM) and thereafter exposed to TFP at the indicated concentrations for 72 h; cell viability was measured by MTT and untreated cells were set to 1. (f) Same as in (e), except cells were pre-treated with BafA1 (1 nM). Data depict mean±S.D. compiled from three independent experiments. Asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference (P<0.05, two-tailed t-test)