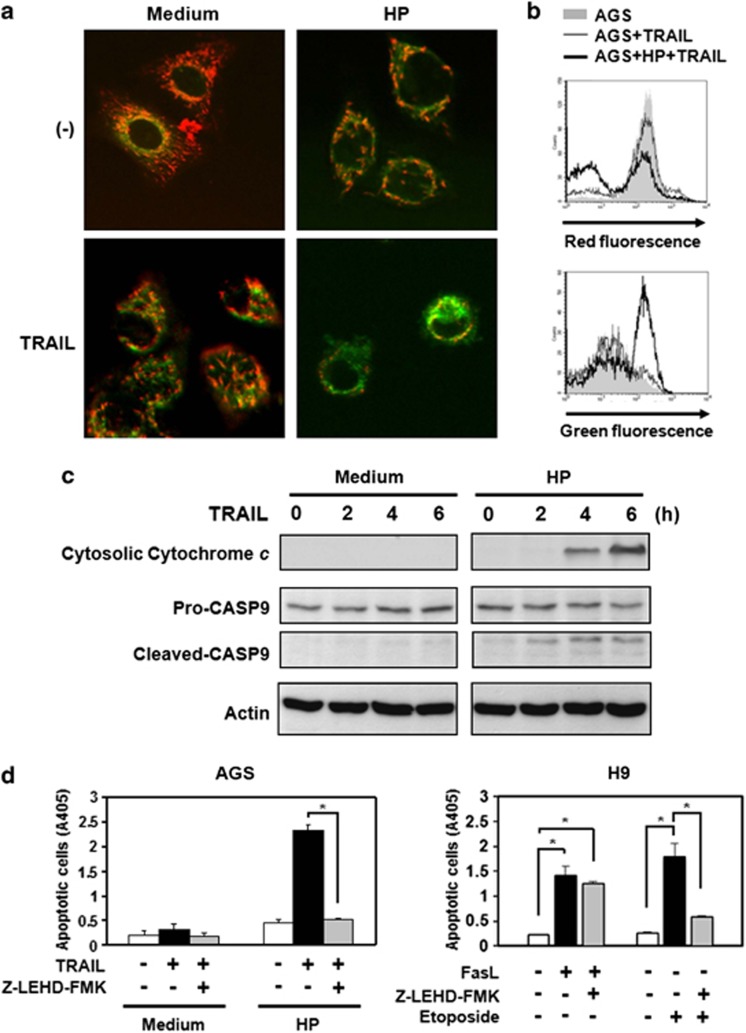
Figure 3.
H. pylori induces activation of the mitochondrial pathway after TRAIL engagement. (a and b) Changes in mitochondrial transmembrane potential were assessed as JC-1 green (uncoupled mitochondria) or red (intact mitochondria) fluorescence. Green fluorescence of JC-1 dye was assessed as a parameter for mitochondrial breakdown. (a) AGS cells were labeled with the mitochondrial transmembrane potential-sensitive dye JC-1 and treated with recombinant TRAIL in the presence or absence of H. pylori. The JC-1 green (uncoupled mitochondria) or red (intact mitochondria) fluorescence was visualized under a confocal microscope. Reduced red fluorescence with increased green fluorescence was observed in AGS cells treated with TRAIL in the presence of H. pylori. There were 100 cells analyzed per field by confocal microscopy, and this is a representative sample. (b) AGS cells were labeled with JC-1 and treated with recombinant TRAIL in the presence or absence of H. pylori. Analysis was performed by a FACS scan. Increased green fluorescence was detectable in AGS cells treated with recombinant TRAIL after exposure to H. pylori (thick line) and compared with AGS cells treated with TRAIL but without exposure to H. pylori (thin line). Shaded histogram: AGS alone. (c) H. pylori induces the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria after TRAIL engagement. AGS cells (106 cells) were incubated with 1 g/ml recombinant TRAIL proteins for various times as indicated in the absence or presence of H. pylori, and the cytoplasmic fraction of the cell lysate was isolated. Cytoplasmic proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Cytochrome c released from mitochondria into the cytoplasm was detected with specific anti-cytochrome c and anti-caspase-9 mAbs (Cell Signaling Technology). The native form of caspase-9 is 47 kDa, and cleaved forms are 37 kDa and 35 kDa. Membranes were also blotted with anti-β-actin mAb as a loading control. The results were representative of at least three independent experiments. (d) AGS Cells were co-cultured with H. pylori and treated with caspase-9 inhibitor, Z-LEHD-fmk, followed by treatment with TRAIL proteins. Cell apoptosis was measured by cell death enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Values represent means±S.D. of three independent experiments (*P<0.05). For specificity control of caspase-9 inhibition by Z-LEHD-fmk, the H9 cells, a type I Fas signaling cells, were treated with FasL (Peprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA), a death stimulus that does not require caspase-9, and Etoposide, a death stimulus that requires caspase-9. Cell apoptosis was measured by cell death ELISA. Values represent means±S.D. of three independent experiments (*P<0.05)