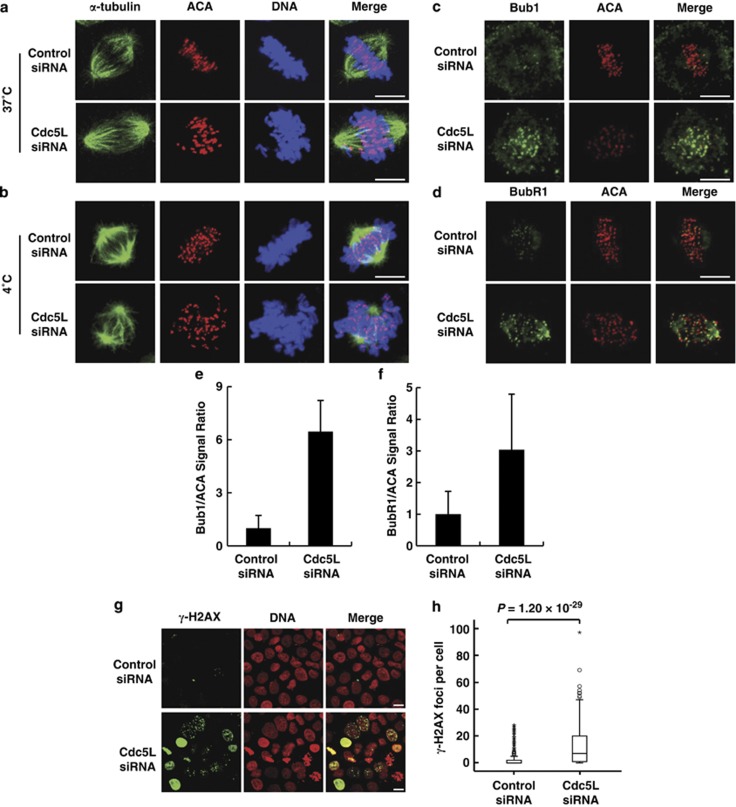
Figure 3.
Depletion of Cdc5L results in kinetochore-microtubule attachment defects and DNA damage. Synchronized HeLa cells transfected with control or Cdc5L siRNA were treated with MG132 to prevent anaphase onset (a–d). Coverslips were chilled on ice for 10 min (b) or fixed immediately (a) and stained with anti-centromere antibody (ACA; for kinetochores; red), anti-α-tubulin antibody (microtubules; green) and SYTOX Blue nucleic acid stain (for DNA; blue), scale bar, 10 μm. For spindle checkpoint analysis(c and d), the cells were stained with anti-Bub1 or BubR1 antibody (green) and ACA (for kinetochores; red), scale bar, 10 μm. (e and f) Quantification of Bub1 and BubR1 levels described as in c and d were analyzed. Bub1 and BubR1 signals were normalized to ACA. For Bub1 quantification, control-knockdown cells (n=4) and Cdc5L-knockdown cells (n=10); for BubR1 quantification, control-knockdown cells (n=7) and Cdc5L-knockdown cells (n=14). Data are shown as mean±S.D. (g) HeLa cells were transfected with control or Cdc5L siRNA, then stained with anti-γ-H2AX antibody (green) and PI (for DNA; red), scale bar, 10 μm. (h) A box-and-whisker plot showing the number of γ-H2AX foci per cell described as in g cells with control siRNA (n=328) or Cdc5L siRNA (n=276). Outliers are indicated by open circles, extremes by asterisks