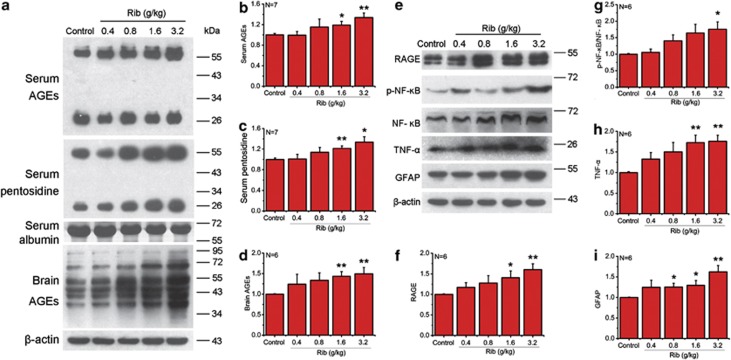
Figure 5.
Intraperitoneal injection of Rib elevates the AGE, RAGE level and production of p-NF-κB, TNF-α, and GFAP in mouse serum and brain. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with Rib in different doses as indicated each day for 10 days. Serum AGEs were detected by western blotting with an anti-AGEs 6D12 monoclonal antibody and an anti-pentosidine monoclonal antibody. Serum albumin level was used as a loading control (a). AGE (a), p-NF-κB, TNF-α, and GFAP level (panel e) of mouse brain were probed by corresponding antibodies. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Quantification results were shown in b–d and f–i, respectively. β-Actin was used as a loading control except that NF-κB p65 activation in each sample was expressed as the ratio of phosphor-NF-κB p65 level to total NF-κB p65 level. The saline control value was set as 1.0. All values are expressed as means±S.E.M. *P<0.05, **P<0.01