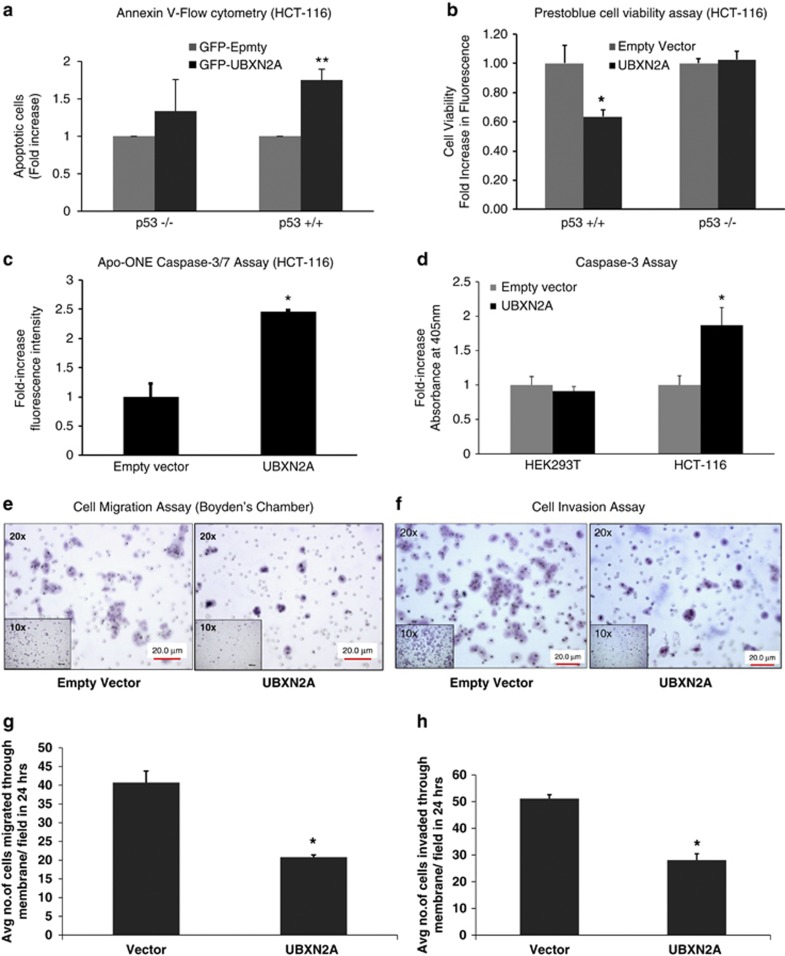
Figure 6.
Induction of apoptosis by UBXN2A is p53 dependent and caspase-mediated in colon cancer cell lines. (a, b) HCT-116 (p53+/+) or HCT-116 (p53−/−) cells were transiently transfected with GFP-empty or GFP-UBXN2A for 48 h. An Annexin V apoptosis assay (a) and Prestoblue cell viability (b) assay show that overexpression of UBXN2A leads to a significant increase in cell apoptosis (c) and reduction of cell viability (d) in HCT-116 with WT-p53 (p53+/+). There was not a significant change between GFP-empty and GFP-UBXN2A in p53-KO cells (*P<0.05, **P<0.01). (c) HCT-116 cells were transfected with GFP-empty or GFP-UBXN2A. After 48 h, levels of caspase-3/7 activity (an indicator of apoptosis) in cells expressing GFP-empty or GFP-UBXN2A were measured using the Apo-ONE homogeneous caspase-3/7 assay kit. Results show 2.5-fold increase in caspase-3/7 activity in cells expressing GFP-UBXN2A relative to GFP-empty cells (*P<0.05). (d) Noncancerous HEK293T cells and HCT-116 colon cancer cell lines were transiently transfected with (His)6-TYG-empty or (His)6-TYG-UBXN2A vectors. A caspase-3 colorimetric assay revealed that UBXN2A exclusively activates caspase-3 only in cancer cells (*P<0.05). (e) Cell migration assay. HCT-116 empty-vector and HCT-116 UBXN2A-expressing cells (300 000 cells/well) were suspended in serum-free medium and seeded on cell culture inserts. After 24 h, cells that migrated through the membrane were stained and photographed at × 20 magnification. Cells were counted in five different fields and the average was plotted. (f) Invasion assay. HCT-116 empty vector and HCT-116 UBXN2A-expressing cells (300 000 cells/well) were suspended in serum-free medium and seeded on Matrigel coated inserts. After 24 h, cells that invaded through the Matrigel insert were stained and photographed at × 20 magnification. Cells were counted in five different fields, and the average was plotted. A representative micrograph (e, f) and quantification (g, h) of invaded cells are shown. The data show a significant decrease in migration/invasion of UBXN2A-expressing cells. For all the assays, data represent the mean of three experiments (Mean±S.E.M.) *P<0.05