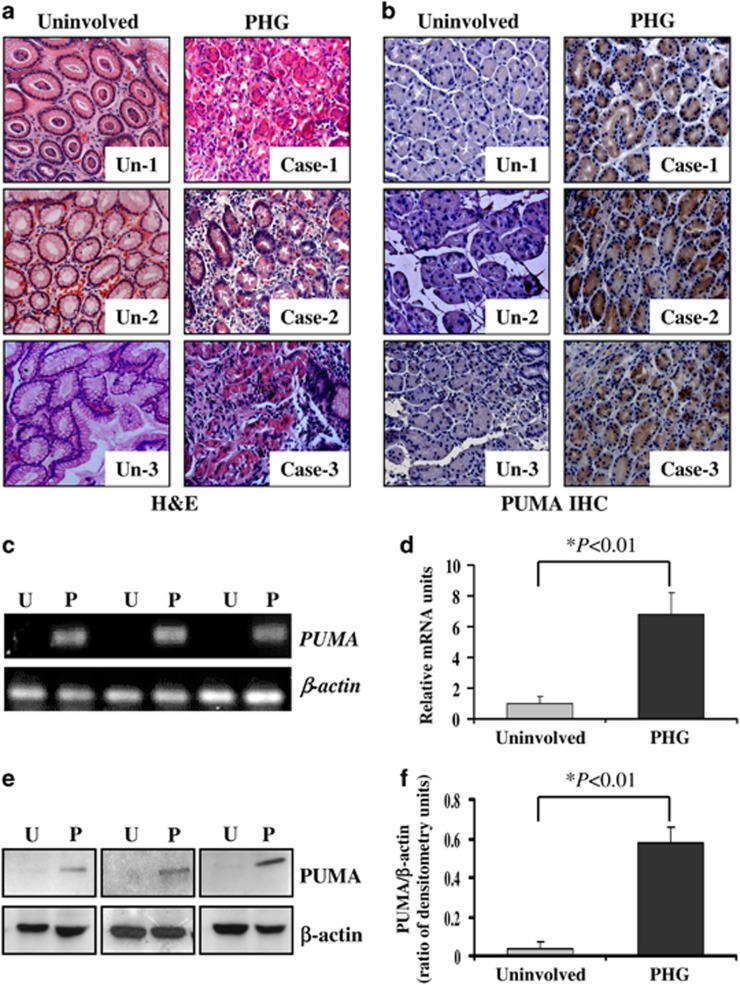
Figure 1.
PUMA was involved in PHG in humans. (a) H&E staining of uninvolved normal gastric mucosal tissues and gastropathic mucosal tissues from three PHG patients ( × 200). (b) PUMA immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining (brown) of uninvolved normal gastric mucosal tissues and gastropathic mucosal tissues from three PHG patients ( × 200). (c) PUMA mRNA expression in the gastric mucosa was evaluated by real-time PCR in three pairs of different specimens. U: uninvolved normal gastric mucosa, P: PHG mucosa. (d) Real-time PCR showed a relative PUMA mRNA fold change in uninvolved normal gastric mucosa and PHG gastric mucosa. The values are expressed as the means±S.D. (n=3 in each group) for real-time PCR. (e) PUMA protein expression in the gastric mucosa was determined by western blotting in three pairs of different specimens. β-Actin was used as the loading control. U: uninvolved normal gastric mucosa, P: PHG mucosa. (f) The ratio of densitometry units of PUMA/β-actin is represented. The values are expressed as the means±S.D. (n=3 in each group) for western blotting