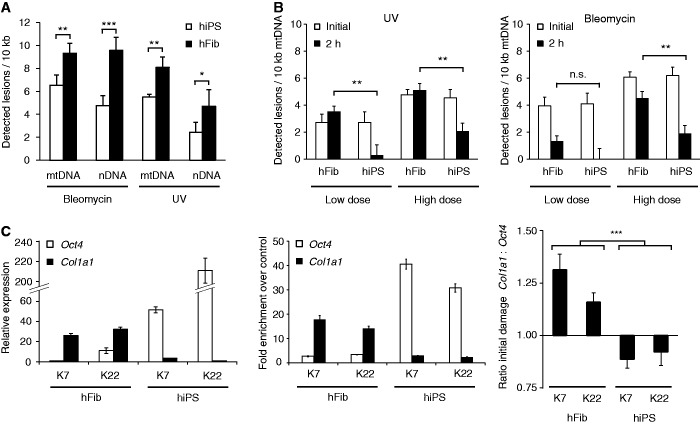
Figure 4.
Exemplary applications of the LORD-Q method. (A) Comparative analysis of genotoxic vulnerability. Human primary fibroblasts (hFib) and corresponding isogenic hiPS cells were treated in serum-free medium with 10 µM bleomycin (20 min) or 10 mJ/cm2 UVC radiation before mitochondrial and genomic lesion rates were determined by LORD-Q analysis (n = 3, mean ± SD). (B) Investigation of mtDNA repair. Human primary fibroblasts and corresponding isogenic hiPS cells were treated with low and high doses of bleomycin (see Materials and methods section for details) or UV radiation in serum-free medium, and then harvested either directly after treatment (indicated ‘initial’) or after 2 h of recovery under cell culture conditions (n = 3, mean ± SD). (C) Comparison of DNA damage in different genes. QRT-PCR expression analysis of Oct4 and Col1a1 in fibroblasts and corresponding hiPS cells (left, n = 3, mean ± SD). Corresponding qPCR analysis of histone H3 acetylation in ChIP-enriched Oct4 and Col1a1 loci (middle). Fibroblasts and corresponding hiPS cell clones were stimulated with 10 µM bleomycin (20 min) and the DNA lesion rates in both Oct4 and Col1a1 gene loci were determined (right, n = 6, mean ± SD). The ratio of detected lesions per 10 kb in both genes is shown. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.