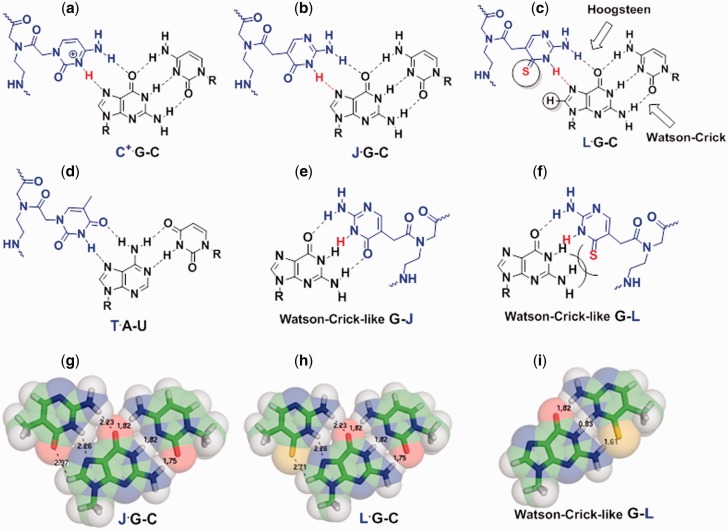
Figure 1.
Chemical structures and structural models of base triples and base pairs formed between PNA (blue) and RNA (black). H3 and S4 atoms in bases C+, J and L are shown in red. (a–d) Chemical structures of base triples of C+∙G–C, J∙G–C, L∙G–C and T∙A–U. L has an enhanced van der Waals interaction with G in a Hoogsteen-like L∙G pair. (e–f) Chemical structures of Watson–Crick-like G–J and G–L pairs. (g–i) Structural models of base triples J∙G–C, L∙G–C and Watson–Crick-like G–L pair. The three dimensional coordinates are based on a C+∙G–C base triple from (26), assuming the structures do not change upon chemical modifications of base C. The numbers shown are inter-atomic distances in Å. van der Waals radii of N, O, S atom groups are ∼1.6, 1.5 and 1.8 Å, respectively (27). A steric clash occurs between G and L in a Watson–Crick-like G–L pair, if the base pairing interface of the G–L pair is maintained the same shape as that of a Watson–Crick G–C pair.