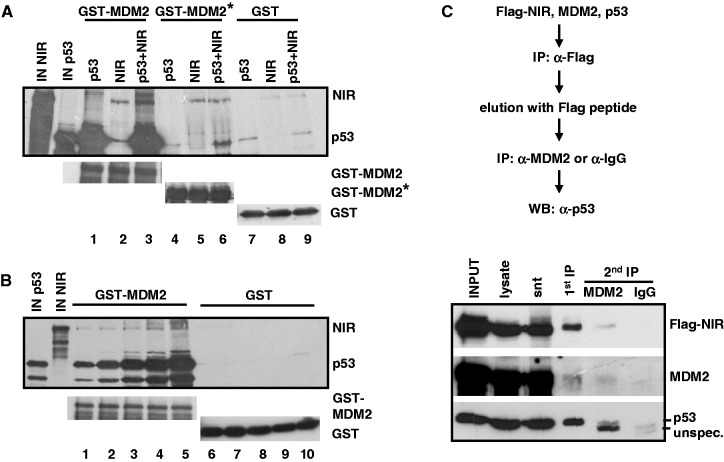
Figure 8.
NIR can form a ternary complex with p53:MDM2. (A) MDM2 central domain (aa 222–366) that does not bind efficiently to p53 retained p53 in the presence of NIR in pull-down assays. 35S-labelled NIR and p53 were incubated with bacterially produced GST, GST-MDM2 or GST-MDM2 222-366 (= MDM2*). IN NIR and IN p53 indicate input controls. Lower panels show the levels of the bacterially expressed GST proteins. (B) NIR associates with GST-MDM2 in dependence of prebound p53 in pull-down assays. GST-MDM2 beads were loaded with increasing amounts of labelled p53, and were then incubated with constant amounts of labelled NIR. IN NIR and IN p53 indicate input controls. Lower panels show the levels of the bacterially expressed GST proteins. (C) Precipitation of a ternary Flag-NIR:MDM2:p53 complex from transfected cells. The flow diagram outlines the experimental procedure. H1299 cells were transfected to produce Flag-NIR, MDM2 and p53. Flag-NIR and associated proteins were precipitated in a first immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Flag antibody (α-Flag) covalently linked to beads. The Flag-NIR complexes were removed from the antibodies with Flag peptide. In a second IP, the complexes were precipitated with a mixture of anti-MDM2 antibodies 3G9 and H221 or incubated with irrelevant antibody (α-IgG). Coprecipitation of p53 was analysed by standard western immunoblotting with the highly sensitive, peroxidase-conjugated anti-p53 antibody DO-1 (1:5000). The other proteins were detected with anti-MDM2 antibody H221 (1:1000) and anti-Flag antibody (1:10 000). snt, supernatant; unspec., unspecific signal.