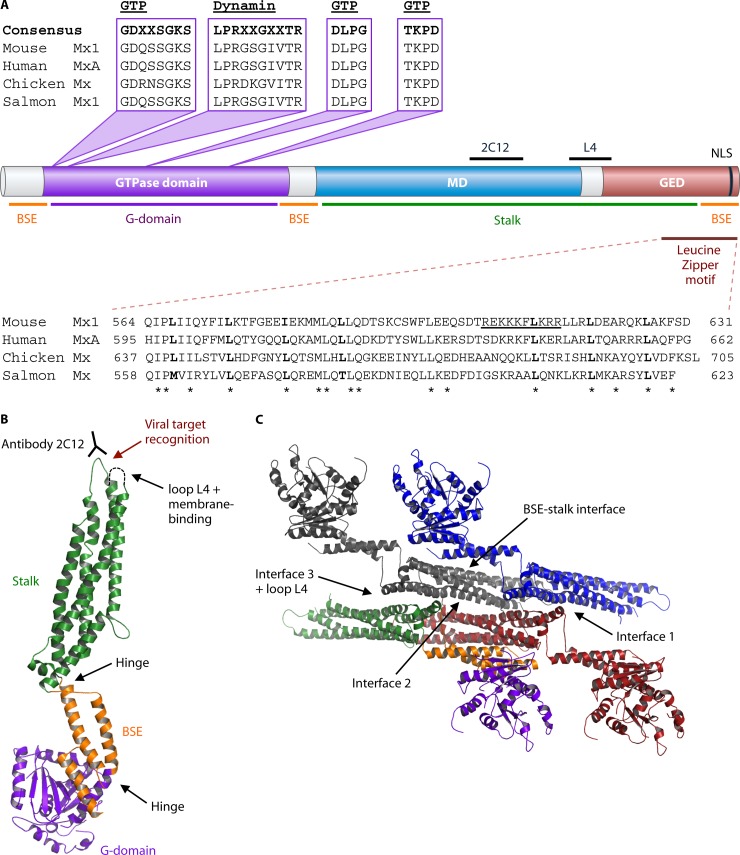
Fig 1.
Structure of Mx proteins. (A) The different domains of Mx proteins delineated by their primary sequence and their relationship to the domains determined in the 3D structure of Mx proteins. The Mx domains in the primary sequence include the GTPase domain, the middle domain (MD), and the GTPase effector domain (GED). The domains in the 3D structure include the G domain, the bundle signaling element (BSE), and the stalk domain. The amino acid sequences of domains important for the antiviral activity of Mx proteins are aligned. These domains include the GTP-binding motif, the dynamin signature, the C-terminal leucine zipper, and the nuclear localization signal (NLS). The conserved amino acids in the leucine zipper are indicated with an asterisk. The position of the epitope recognized by the monoclonal antibody 2C12, which can neutralize Mx antiviral activity, is indicated above the MD. The 2C12 epitope and loop L4 are important for viral target recognition. (B) 3D structure of Mx proteins (PDB file MxA 3SZR [73]). (C) 3D structure of MxA tetramer showing the interfaces (1 to 3 and loop L4) involved in oligomer formation (65, 73, 109). The images in panels B and C were generated with PyMOL.