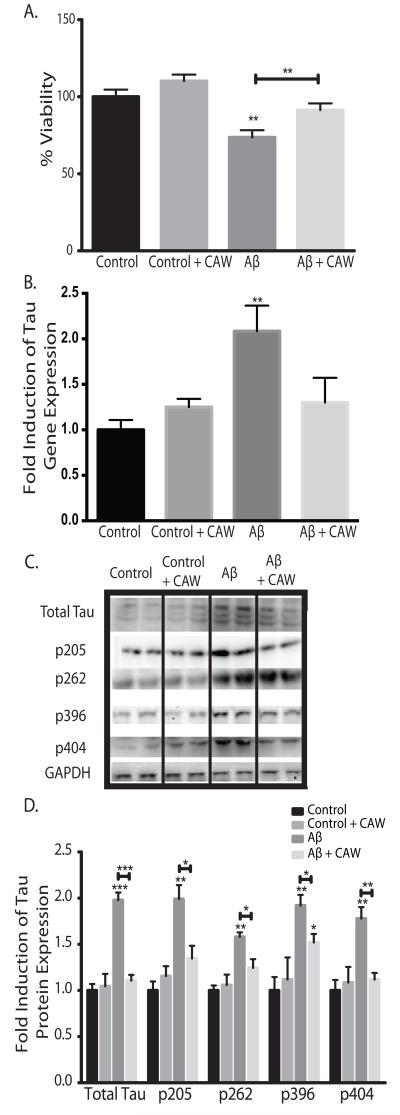
Figure 2.
CAW attenuates the effects of extracellular Aβ peptide administration in SH-SY5Y cells. *p<0.05, **p<0.1, ***p<0.001 relative to control unless otherwise indicated. A) Aβ25-35 treatment (50uM) significantly reduced cell viability but this effect was partially attenuated by CAW (100ug/mL). n=16-24 per treatment condition. B) Aβ25-35 treatment (50uM) significantly increased tau gene expression and CAW (100ug/mL) prevented this effect. n=6-8 per treatment condition. C) Aβ25-35 treatment (50uM) also increased tau protein expression and phosphorylation at several sites. CAW (100ug/mL), added to Aβ25-35 treatment, reduced these increases in total tau protein as well as phosphorylation at each site. Each immunoblot image is a grouping of representative images from different parts of the same gel. D) Densitometric analysis of 4-5 separate blots per treatment condition. Optical densities were normalized to GAPDH and fold induction is calculated relative to the control condition.