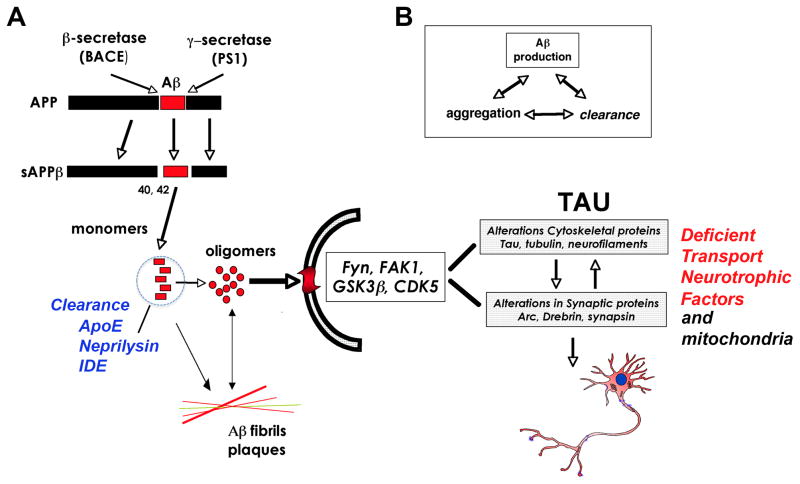
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing the processing of APP, the formation of Aβ oligomers, and its interaction with Tau in the mechanisms of synapse loss. A) APP is cleaved by β and γ-secretases to form sAPPβ. Monomeric Aβ42 can form Aβ oligomers that can be cleared by ApoE and proteases such as neprilysin and IDE. Both Aβ monomers and oligomers progress to fibrils and plaques, while Aβ oligomers interact with surface receptors that in turn activate various kinases to alter Tau, leading to loss of axonal transport of neurotrophic factors and impaired mitochondrial function, culminating in neurotoxicity. B) Aβ production is dependent on both Aβ clearance, aggregation and synthesis.