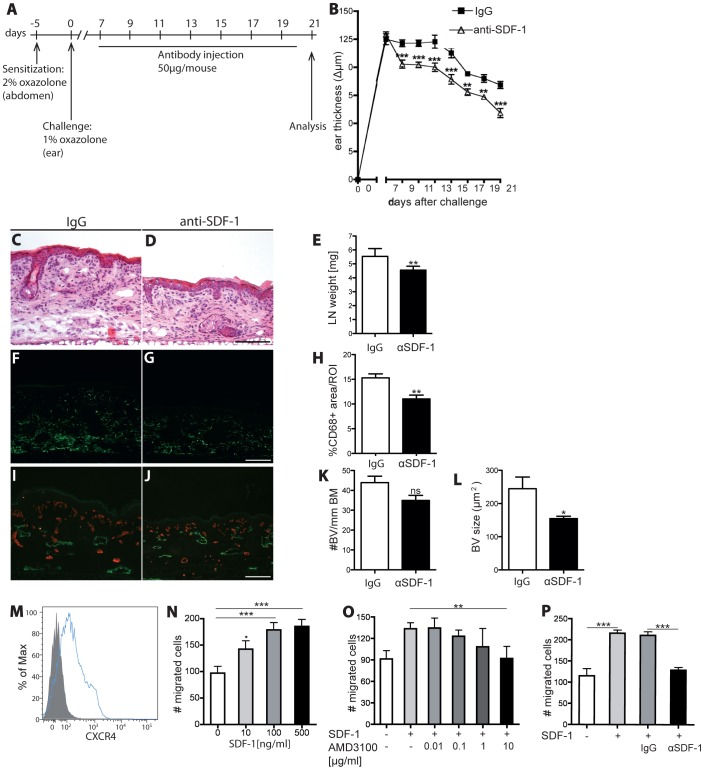
Figure 4. Inhibition of SDF-1 signaling alleviates chronic skin inflammation and inhibits leukocyte migration towards SDF.
(A) On day -5, hemizygous K14 VEGF-A transgenic mice (n = 14) were sensitized with 2% oxazolone and challenged on day 0 with 1% oxazolone on the ears. Starting 7 days after challenge, mice received i.v injections of anti-SDF-1 antibody or isotype-matched IgG every second day. (B) Neutralization of SDF-1 (△) significantly reduced inflammatory ear swelling as compared with IgG-injected mice (□). Data represent mean ±SEM. (C-D) H&E stains of mouse ear sections at day 21 showed reduced edema and inflammatory cell infiltration in the anti-SDF-1 treated mice (D) in comparison to the IgG control group (C). One ear half is shown. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (E) In anti-SDF-1 treated mice, the weight of ear draining LNs was significantly reduced compared with controls. (F-H) Immunofluorescence staining for CD68 revealed a significant reduction in the percentage of area covered by macrophages in anti-SDF-1-treated animals as compared to IgG treatment. (I-L) Neutralization of SDF-1 decreased the size and numbers of blood vessels in the inflamed ear skin. (M) FACS analysis of CD11b+ splenocytes revealed a clear expression of CXCR4 on their surface. (N) SDF-1 promoted the chemotactic migration of CD11b+ splenocytes in vitro. (O-P) The chemotactic effect of SDF-1 was blocked by incubation with AMD3100 (O) or with an anti-SDF-1 antibody (P), but not with control IgG. Two independent experiments were performed. Data represent mean±SD. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.